missouri

 René-Auguste Chouteau Jr, who was best known as Auguste Chouteau, was the founder of Saint Louis, Missouri. While being a founder of a city is not necessarily such a strange thing, the way in which it came about is not so common. He was the only child of Marie-Thérèse (nee Bourgeois) and René Chouteau, born in either September 7th of either 1749 or 1750. René purportedly abused Marie-Thérèse, and abandoned her and René, so she returned to her pre-matrimonial home. She later remarried. In 1764, when Auguste was still a young man of just 13 years, his stepfather, Pierre Liguest sent him up the Missouri River from Fort Chartres, Illinois. Auguste was the leader of a company of 30 men. His mission was to select a site for a trading post. His stepfather must have considered the young man to be quite intelligent to put him in charge of such an enormous undertaking. Auguste didn’t let his stepfather down either. He chose a place that was not only perfect for the trading post, but would later become a great American city…Saint Louis, Missouri. After his stepfather’s death in 1778, Auguste succeeded him in the business and later formed a partnership with John Jacob Astor. Together they formed the American Fur Company. Auguste was 29 years old.
René-Auguste Chouteau Jr, who was best known as Auguste Chouteau, was the founder of Saint Louis, Missouri. While being a founder of a city is not necessarily such a strange thing, the way in which it came about is not so common. He was the only child of Marie-Thérèse (nee Bourgeois) and René Chouteau, born in either September 7th of either 1749 or 1750. René purportedly abused Marie-Thérèse, and abandoned her and René, so she returned to her pre-matrimonial home. She later remarried. In 1764, when Auguste was still a young man of just 13 years, his stepfather, Pierre Liguest sent him up the Missouri River from Fort Chartres, Illinois. Auguste was the leader of a company of 30 men. His mission was to select a site for a trading post. His stepfather must have considered the young man to be quite intelligent to put him in charge of such an enormous undertaking. Auguste didn’t let his stepfather down either. He chose a place that was not only perfect for the trading post, but would later become a great American city…Saint Louis, Missouri. After his stepfather’s death in 1778, Auguste succeeded him in the business and later formed a partnership with John Jacob Astor. Together they formed the American Fur Company. Auguste was 29 years old.
Chouteau married Marie Therese, the daughter of Jean-Gabriel Cerré, on September 21, 1786, at the Basilica of Saint Louis, King of France, which was a vertical-log church…long since replaced with the current church on the site. The apparently happy marriage united members of the two leading Saint Louis families. They were renowned for their hospitality, which helped strengthen his political position in the city and region. Together they had seven children…Auguste Aristide, Gabriel, Marie Thérèse Eulalie, Henry, Edward, Louise, and Emilie.
Auguste was commissioned colonel of the militia in 1808. His political career began in 1815 when he was appointed one of the commissioners to make treaties with the Indians who had fought on the British side in the War of 1812. The other two commissioners were Ninian Edwards and William Clark. I don’t suppose this would be a big step into politics, but it was an office, and the field of politics seems to take off from a smaller office. 
 In Saint Louis, he served as Justice of the Peace and as Judge of the Court of Common Pleas. He was also the first president of the Bank of Missouri, as well as several other important positions. Auguste made it his policy when dealing with the Indians, to treat them fairly. Because of that, he enjoyed their confidence and friendship until his death, which occurred on February 24, 1829.
In Saint Louis, he served as Justice of the Peace and as Judge of the Court of Common Pleas. He was also the first president of the Bank of Missouri, as well as several other important positions. Auguste made it his policy when dealing with the Indians, to treat them fairly. Because of that, he enjoyed their confidence and friendship until his death, which occurred on February 24, 1829.

 It was inevitable really…the migration of the people of the United States to the west coast, in search of gold, adventure, and more land. The east was filling up, and there was no place else to go, but west. Of course, many people would either not make it all the way to the West; choosing rather to homestead along the way, die, or actually make it to the West, and then return to the East. Nevertheless, before anyone could find out is life on the west coast suited them or not, they had to get to the west coast, and on May 16, 1842, the first major wagon train to the northwest departed from Elm Grove. Missouri, on the Oregon Trail. This was a little bit of a risky move, because US sovereignty over the Oregon Territory was not clearly established until 1846.
It was inevitable really…the migration of the people of the United States to the west coast, in search of gold, adventure, and more land. The east was filling up, and there was no place else to go, but west. Of course, many people would either not make it all the way to the West; choosing rather to homestead along the way, die, or actually make it to the West, and then return to the East. Nevertheless, before anyone could find out is life on the west coast suited them or not, they had to get to the west coast, and on May 16, 1842, the first major wagon train to the northwest departed from Elm Grove. Missouri, on the Oregon Trail. This was a little bit of a risky move, because US sovereignty over the Oregon Territory was not clearly established until 1846.
Nevertheless, American fur trappers and missionary groups had been living in the region for decades, along with Indians who had settled the land centuries earlier. Of course, everyone out there had a story to tell, and there were dozens of books and lectures that proclaimed Oregon’s agricultural potential. You can’t tell a story without creating interest somewhere. Even a boring story is of interest to someone, and this was no boring story. With the books and lectures coming out of the West, the white American farmers were very interested. They saw a chance to make their fortune, or at least to become independent. The actual first overland immigrants to Oregon, intended to farm primarily. A small band of 70 pioneers left Independence, Missouri in 1841. The stories they had heard from the fur traders brought them along the same route the traders had blazed, taking them west along the Platte River through the Rocky Mountains via the easy South Pass in Wyoming and then northwest to the Columbia River…basically through some on my own stomping grounds. Eventually, the trail they took was renamed by the pioneers, who called it the Oregon Trail.
The migration, once started, had little chance of being stopped, and in 1842, a slightly larger group of 100 pioneers made the 2,000-mile journey to Oregon. With the success of these two groups, the inevitable happened, accelerated in a major way by the severe depression in the Midwest, combined with a flood of propaganda from fur traders, missionaries, and government officials extolling the virtues of the land. They may have had good intentions, but it is never a good idea to lie to the public. With the disinformation on their minds, farmers dissatisfied with their prospects in Ohio, Illinois, Kentucky, and Tennessee, hoped to find better lives in the supposed paradise of Oregon. With that another type of “rush” began. Much like the “gold rush” years, the farmers saw the land as their “gold” and headed west.
So, on this day in 1843, approximately 1,000 men, women, and children climbed aboard their wagons and steered their horses west out of the small town of Elm Grove, Missouri. It was the first real wagon train, comprised of more than 100 wagons with a herd of 5,000 oxen and cattle trailing behind. The train was led by Dr Elijah White, a Presbyterian missionary who had made the trip the year before. At first the trail was fairly easy, traveling over the flat lands of the Great Plains. There weren’t many obstacles in that area, and few river crossings, some of which could be dangerous for wagons. The bigger risk in the early days was the danger of Indian attacks, but they were still few and far between…at first anyway. The wagons were drawn into a circle at night to give the pioneers better protection from any attack that might come. They were very afraid of the Indians, who were enough different that they seemed deadly…to the pioneers anyway, and the Indians fear the White Man because of their weapons, and they were angry because the White Man wanted the land. In reality, the pioneers were far more in danger from seemingly mundane causes, like the accidental discharge of firearms, falling off mules or horses, drowning in river crossings, and disease. The trail became much more difficult, with steep ascents and descents over rocky terrain, after the train entered the mountains. The pioneers risked injury from overturned and runaway wagons.
Nevertheless, the wagon trains persevered, and the migrant movement continued until the West was populated. As for the 1,000-person party that made that original journey way back in 1843…the vast majority survived to reach their destination in the fertile, well-watered land of western Oregon. The next migration, in 
 1844 was smaller than that of the previous season, but in 1845 it jumped to nearly 3,000. Migration to the West was here to stay and the trains became an annual event, although the practice of traveling in giant convoys of wagons soon changed to many smaller bands of one or two-dozen wagons. The wagon trains really became a thing of the past in 1884, when the Union Pacific constructed a railway along the route.
1844 was smaller than that of the previous season, but in 1845 it jumped to nearly 3,000. Migration to the West was here to stay and the trains became an annual event, although the practice of traveling in giant convoys of wagons soon changed to many smaller bands of one or two-dozen wagons. The wagon trains really became a thing of the past in 1884, when the Union Pacific constructed a railway along the route.
 William T Anderson’s life was always rather a violent one, but it escalated when his sister died while in the custody of the Union soldiers during the Civil War. Anderson was born around 1840 in Hopkins County, Kentucky, to William and Martha Anderson. His siblings were Jim, Ellis, Mary, Josephine, and Martha. His schoolmates recalled him as a well-behaved, reserved child, so they might be surprised to see how he ended up. Anderson began to support himself early on, by stealing and selling horses in 1862. After a Union loyalist judge killed his father, Anderson killed the judge and fled to Missouri. He was always one to exact revenge for anything in which he felt that he or his family were wronged. In Missouri, he robbed travelers and killed several Union soldiers.
William T Anderson’s life was always rather a violent one, but it escalated when his sister died while in the custody of the Union soldiers during the Civil War. Anderson was born around 1840 in Hopkins County, Kentucky, to William and Martha Anderson. His siblings were Jim, Ellis, Mary, Josephine, and Martha. His schoolmates recalled him as a well-behaved, reserved child, so they might be surprised to see how he ended up. Anderson began to support himself early on, by stealing and selling horses in 1862. After a Union loyalist judge killed his father, Anderson killed the judge and fled to Missouri. He was always one to exact revenge for anything in which he felt that he or his family were wronged. In Missouri, he robbed travelers and killed several Union soldiers.
Anderson became a guerrilla, when his family was living in Council Grove, Territory of Kansas at the start of the Civil War. After William Quantrill’s raid on Aubry, Kansas on March 7, 1862, a Federal company from Olathe, Kansas sent a patrol from Company D, Eighth Kansas Jayhawker Regiment to investigate. Their mission was to seek out Southern sympathizers living nearby, who might be accused of aiding the raiders. Anderson’s father and uncle were named as such, and when the Jayhawker company arrived at the Anderson farm on March 11th, William and his younger brother Jim were delivering 15 head of cattle to the US commissary agent at Fort Leavenworth. When the brothers returned to their farm, they found their father and uncle hanged in retaliation, their home burned to the ground, and all their possessions stolen. It was an act of war in their minds, because the men had no chance to defend themselves. Two days later Bill and his brother Jim were both riding with Quantrill’s Raiders, a group of Confederate guerrillas operating along the Kansas–Missouri border. Anderson moved his sisters from Kansas, and for a year they lived at various places stopping finally with the Mundy family on the Missouri side of the line near Little Santa Fe. When asked why he joined Quantrill, Anderson replied by saying, “I have chosen guerrilla warfare to revenge myself for wrongs that I could not honorable revenge otherwise. I lived in Kansas when this war commenced. Because I would not fight the people of Missouri, my native State, the Yankees sought my life but failed to get me. [They] revenged themselves by murdering my father, [and] destroying all my property.”
Anderson became a skilled bushwhacker and quickly earned the trust of the group’s leaders, William Quantrill and George M Todd. It was his bushwhacking skills that ultimately marked him as a dangerous man…and eventually led the Union to imprison his sisters. Then, after a building collapse in the makeshift jail in Kansas City, Missouri, left one of his sisters dead, while in custody and the others permanently maimed, Anderson devoted himself to revenge. He took a leading role in the Lawrence Massacre and later took part in the Battle of Baxter Springs, both in 1863. He later satisfied his revenge by hijacking a train full of Union troops and slaughtering 24 of them, thus giving him the name “Bloody Bill” Anderson.
By 1863, all Bill had left was a brother and two sisters, who had miraculously survived the August 13 Union jail collapse in Kansas City. The collapse wasn’t an accident. Union guards from the 9th Kansas Jayhawker Regiment, serving as provost guards in town, intentionally collapsed a three-story brick building on a number of young Southern female prisoners. Fourteen-year-old Josephine Anderson was killed in the collapse. Bill’s ten-year-old sister Martha’s legs were horribly crushed crippling her for life, and his sixteen-year-old sister Mary suffered serious back injuries and facial lacerations. Both girls would carry their physical and emotional scars for the rest of their lives. War is an ugly thing, and unfortunately, sometimes unscrupulous people do things  they shouldn’t. The atrocity at the jail was a war crime and should have been punished as such, but I suppose that didn’t justify the murders that followed, because there was no proof that those murdered were involved in any way.
they shouldn’t. The atrocity at the jail was a war crime and should have been punished as such, but I suppose that didn’t justify the murders that followed, because there was no proof that those murdered were involved in any way.
Union military leaders ordered Lieutenant Colonel Samuel P Cox to kill Anderson and provided him with a group of experienced soldiers. A local woman saw Anderson soon after he left Glasgow and told Cox where he was. On October 26, 1864, Cox pursued Anderson’s group with 150 men and engaged them in a battle called the Skirmish at Albany, Missouri. Anderson and his men charged the Union forces, killing five or six of them, but turned back under heavy fire. Only Anderson and one other man, the son of a Confederate general, continued to charge after the others had retreated. Anderson was hit by a bullet behind an ear, which most likely killed him instantly. Four other guerrillas were killed in the attack as well. The victory made a hero of Cox and led to his promotion.
 Shortly after President Thomas Jefferson completed the Louisiana Purchase from France, which made it an American territory, William Ashley, who was a Virginia native, made the decision to move to Missouri. Ashley was a young man, who was looking to make a name for himself. He entered into a partnership with Andrew Henry to manufacture gunpowder and lead. Opportunists, Ashley and Henry took advantage of the fact that these two commodities were in short supply in young America.
Shortly after President Thomas Jefferson completed the Louisiana Purchase from France, which made it an American territory, William Ashley, who was a Virginia native, made the decision to move to Missouri. Ashley was a young man, who was looking to make a name for himself. He entered into a partnership with Andrew Henry to manufacture gunpowder and lead. Opportunists, Ashley and Henry took advantage of the fact that these two commodities were in short supply in young America.
Ashley’s business prospered during the War of 1812, and he also joined the Missouri militia. He eventually achieved the rank of general. When Missouri became a state in 1822, Ashley used his military fame, and his business success to win election at lieutenant governor. Once elected, Ashley set about looking for opportunities to enrich both Missouri and his own pocketbook. Because he knew the area, he realized that Saint Louis was in a perfect place to exploit the fur trade on the upper Missouri River.
Ashley recruited his old business partner, Henry to join him in this new venture. Then, Ashley placed an advertisement in the Missouri Gazette and Public Advisor seeking 100 “enterprising young men” to engage in fur trading on the Upper Missouri. The advertisement was a big success. Scores of young men responded and came to Saint Louis. Among them were such future legendary mountain men as Jedediah Smith and Jim Bridger, as well as the famous river man Mike Fink. In time, these men and dozens of others would go on to uncover many of the geographic mysteries of the Far West, but for now they were looking to make a living trapping animals for their furs.
1822 found Ashley and a small band of his fur trappers building a trading post on the Yellowstone River in Montana in order to expand outward from the Missouri River. The Arikara Indians didn’t like this invasion, and they were deeply hostile to Ashley’s attempts to undercut their long-standing position as middlemen in the fur trade. The ensuing attacks eventually forced the men to abandon the Yellowstone post. Out of desperation, Ashley hit on a new strategy. Instead of building central permanent forts along the major rivers, he decided to send his trappers overland in small groups traveling by horseback. By avoiding the river arteries, the trappers could both escape detection by hostile Indians and develop new and untapped fur regions. Almost by accident, Ashley invented the famous “rendezvous” system that revolutionized the American fur trade. The necessary supplies were delivered and furs were delivered at meetings in a large meadow near the Henry’s Fork of Wyoming’s Green River in the early summer of 1825.
Ashley’s first fur trapper rendezvous was very successful. Ashley took home a tidy profit for his efforts. The fur  trappers not only had an opportunity to trade for supplies, but a chance to enjoy a few weeks of often drunken socializing. Ashley organized a second highly profitable rendezvous in 1826, and then decided to sell out. While he was no longer a part of it, his rendezvous system continued to be used by others. The system eventually became the foundation for the powerful Rocky Mountain Fur Company. With plenty of money in the bank, Ashley was able to return to his first love…politics. He was elected to Congress three times and once to the Senate, where he helped further the interests of the western land that had made him rich.
trappers not only had an opportunity to trade for supplies, but a chance to enjoy a few weeks of often drunken socializing. Ashley organized a second highly profitable rendezvous in 1826, and then decided to sell out. While he was no longer a part of it, his rendezvous system continued to be used by others. The system eventually became the foundation for the powerful Rocky Mountain Fur Company. With plenty of money in the bank, Ashley was able to return to his first love…politics. He was elected to Congress three times and once to the Senate, where he helped further the interests of the western land that had made him rich.
 Deadwood, South Dakota maybe started out as an illegal town, but once it was established, there came a need for things like mail, supplies, and transportation, the latter of which brought the need for a stagecoach. The biggest problem with the stagecoach was the fact that the lawless element in the area thought it would be an easy target for robbery. The stagecoaches became a ride for the very brave. Soon it became apparent that the stagecoaches were going to need some protection.
Deadwood, South Dakota maybe started out as an illegal town, but once it was established, there came a need for things like mail, supplies, and transportation, the latter of which brought the need for a stagecoach. The biggest problem with the stagecoach was the fact that the lawless element in the area thought it would be an easy target for robbery. The stagecoaches became a ride for the very brave. Soon it became apparent that the stagecoaches were going to need some protection.
Daniel “Boone” May was born in Missouri in 1852. Going by the name of “Boone,” he was the son of Samuel and Nancy May, the seventh of nine children. Later, he moved with his family to Bourbon County, Kansas, where his father worked as a farmer. In 1876, “Boone” and his older brother moved to Cheyenne, Wyoming, where they worked in the freight business. During this time, the Black Hills were crawling with road agents and hostile Sioux Indians.It was a dangerous time to be working along the roadways in that area. Nevertheless, May did very well there, and he decided to buy a ranch between the Platte River and Deadwood by the end of that year.
“Boone’s” bravery and work ethic soon came to the attention of the stagecoach service, and he was soon recruited as a shotgun messenger for the Cheyenne and Black Hills Stage & Express Company. He also served as the station keeper at Robbers’ Roost in Wyoming Territory. Within just a few years, “Boone” was thought to have been in at least eight shooting incidents with outlaws. Many people said that he was the fastest gun in the Dakotas. His adventures soon became well known.
One of the first hold-ups “Boone” was involved in was in August, 1877, when a Deadwood Coach was intercepted at Robber’s Roost. On this occasion, even though “Boone” wanted to fight it out, he decided to lay down his weapons, because a woman and child were in the coach. The robbers made away with the passenger’s money, weapons and personal property. While they lost their things, I’m sure they decided that it was best to walk away with their lives. A short time later, “Boone” ran into one of the bandits, a man named Prescott Webb, in Deadwood and within no time, gunfire erupted between the two men. Though “Boone” was hit in the left wrist, he returned fire as Webb jumped on a horse to make his getaway. “Boone’s” shots hit Webb in the shoulder, and the horse several times, bringing it down. Webb was quickly arrested by Sheriff Seth Bullock and later that day, Webb’s companions who had aided in the robbery, were also arrested.
In 1878, stagecoaches known as “treasure coaches” were running regularly between Deadwood and Cheyenne. Their cargo was strong boxes filled with gold, as well as the U.S. Mail. These “treasure coach” stages often became the target of bandits, and after one of these coaches was held up on July 2, 1878, the U.S. Postal Service appointed a number of special agents to bring the outlaws to justice. “Boone” and ten other men were soon appointed as U.S. Deputy Marshals and equipped with good horses and ammunition. One of “Boone’s” first encounters with bandits as a U.S. Deputy Marshal occurred on the night of September 13, 1878. He and another messenger were trailing a Cheyenne bound coach which was approached by bandits near Old Woman’s Creek in the Wyoming Territory. “Boone” and another deputy, Zimmerman surprised the outlaws and shooting erupted. “Boone” wounded one bandit named Frank Towle and the others fled empty handed. Leaving their Towle wounded on the ground, the two messengers went after the other bandits but were unable to capture them. When they returned to the robbery site, Towle was gone.
On September 26, 1878, when “Boone” and other messengers were waiting to escort a coach at Beaver Station on the Wyoming-Dakota border, but the stage failed to show up. They went in search of the coach, and met another messenger who told them it had been robbed and a passenger killed. “Boone” quickly joined a posse to go after the outlaws, but they escaped. The following month, “Boone” learned of the hiding place of a robber named Archie McLaughlin and quickly went after him and his gang. Capturing them north of Cheyenne, the outlaws were sent under guard to Deadwood on the northbound coach. Unfortunately, the stage never make it, because on November 3, 1878, it was stopped by vigilantes who hanged Archie McLaughlin and another man named Billy Mansfield. The next month, “Boone” was in a posse that brought in a robber named Tom Price. The bandit tried to escape, and was wounded, and then was brought in. Late in 1879, “Boone” was sent to assist Special Agent William Llewellyn in the capture of a mail robber named Curley Grimes. They tracked the outlaw  to Elk Creek, located halfway between Rapid City and Fort Meade where they arrested him. That night, as the group neared Fort Meade, Grimes attempted to escape and was shot and killed by “Boone” and Llewellyn. By this time, “Boone” had made such a reputation for himself that he became a target for many of the outlaws who repeatedly tried to assassinate him, unsuccessfully. “Boone” also worked as a messenger for the Black Hills Placer Mining Company in the summer of 1880, and was said to have killed at least one robbers during this time. A short time later, “Boone” resigned from the company and left the Black Hills. He turned up in Santiago, Chili in 1883. He shot an army officer in 1891, he fled to Brazil. He died of yellow fever in Rio de Janeiro in 1910.
to Elk Creek, located halfway between Rapid City and Fort Meade where they arrested him. That night, as the group neared Fort Meade, Grimes attempted to escape and was shot and killed by “Boone” and Llewellyn. By this time, “Boone” had made such a reputation for himself that he became a target for many of the outlaws who repeatedly tried to assassinate him, unsuccessfully. “Boone” also worked as a messenger for the Black Hills Placer Mining Company in the summer of 1880, and was said to have killed at least one robbers during this time. A short time later, “Boone” resigned from the company and left the Black Hills. He turned up in Santiago, Chili in 1883. He shot an army officer in 1891, he fled to Brazil. He died of yellow fever in Rio de Janeiro in 1910.
 Myra Belle Shirley was born in a log cabin near Carthage, Missouri on February 5, 1848 to “Judge” John Shirley, and his third wife, Elizabeth “Eliza” Pennington. John Shirley was the black sheep of a well-to-do Virginia family who had moved west to Indiana, where he married and divorced twice. His third wife, Eliza, was on the Hatfield side of the feuding Hatfield and McCoy families, which ranks up there with people I wouldn’t want for parents. The Hatfield and McCoy feuds, while not starting until about 1865, went on for decades, and they were messy and confusing over those years. You might no know who Myra Belle Shirley was, or you might know her best at Belle Starr.
Myra Belle Shirley was born in a log cabin near Carthage, Missouri on February 5, 1848 to “Judge” John Shirley, and his third wife, Elizabeth “Eliza” Pennington. John Shirley was the black sheep of a well-to-do Virginia family who had moved west to Indiana, where he married and divorced twice. His third wife, Eliza, was on the Hatfield side of the feuding Hatfield and McCoy families, which ranks up there with people I wouldn’t want for parents. The Hatfield and McCoy feuds, while not starting until about 1865, went on for decades, and they were messy and confusing over those years. You might no know who Myra Belle Shirley was, or you might know her best at Belle Starr.
Myra grew up in a well to do family, after her father John Shirley made good in 1856 when he and his wife sold their financially successful farming venture raising wheat, corn, hogs, and horses in Jasper County, Missouri. When John sold the land, they opened an inn, a tavern, livery stable and blacksmith shop. Their businesses took up almost an entire city block. John Shirley had become a respected member of the burgeoning county seat of Carthage, and his daughter Myra Belle lived the life of a spoiled, rich girl, attending the Carthage Female Academy, where in addition to the basics, she was taught music and classical languages. She was a bright student, with polite manners, and a talent for playing the piano. However, she also liked to flaunt her status a “rich girl” and liked having an audience. She also loved the outdoors, where she spent many a day roaming the countryside with her older brother Bud, who taught her how to ride a horse and handle a gun…a little out of the ordinary, but still within the confines of a proper upbringing, but dramatic changes were coming for Myra.
When the Kansas-Missouri Border War broke out. Jasper County watched both armies pass through time and again, forcing residents to take sides, and making neighbors into bitter enemies. Irregular bands of “Jayhawkers” and “Red Legs” laid waste to Missouri communities in support of the Union. When son Bud joined Quantrill’s Raiders, John Shirley was a proud father. Bud, who knew the area and the people well, served admirably as a scout, quickly attaining a captain’s rank. But in June 1864 Bud was killed in Sarcoxie, Missouri. The raids had taken their toll on Shirley’s businesses and after Bud’s death, the “Judge” gave up, sold his Missouri property and moved his family to a farm near Scyene, Texas, a small settlement southeast of Dallas.
In 1866 the James-Younger Gang robbed their first bank in Liberty, Missouri, and fled with $6,000 in cash and bonds. Splitting up, Jesse and Frank James, along with the Youngers, fled to Texas, where they met up with Myra Shirley. Soon, Myra became smitten by Cole, quickly becoming a member of their “gang.” One of these outlaw bands, seeking refuge, stayed at the Shirley house one night. Belle later stated that it was there that she became reacquainted with the first man she ever loved. His name was Jim Reed, and she had first met him back in Missouri, where the Reed and Shirley families had been friends. The romance blossomed in Texas, and Belle and Jim married on November 1, 1866. The Shirleys had no objection to the marriage, as Jim Reed was not yet a wanted man. Jim moved into the Shirley household near Scyene and shared the farm chores. Later, he became a salesman for a Dallas saddle and bridle maker. By late 1867, though, he and Belle were living on the Reed homestead in Missouri. Early in September 1868, Belle gave birth to her first child, Rosie Lee. Belle adored the baby and referred to her as her “Pearl.” The nickname stuck. When Jim and Belle moved to Missouri, Reed was a wanted man, allegedly for murdering a man named Shannon. The two fled to California with their young daughter Pearl and before long a second child came along who they named Edward.
In 1869 Belle, Reed and two other outlaws rode to the North Canadian river country, where they tortured an old Creek Indian until he told them where he had hidden $30,000 in gold. With their share of the loot, Jim and Belle returned to Texas, where she played the role of “Bandit Queen” to the hilt. But, it wasn’t long before the outlaw life caught up with Reed and on August 1874, Reed was killed in a gunfight by a member of his own gang. Belle left her children with her mother while she rode the outlaw trail. In Indian Territory (what is now Oklahoma,) Starr got involved with a flat-faced Indian outlaw who went by the name of “Blue Duck.” Of her life, Belle Starr stated to The Fort Smith Elevator about one year prior to her death, “I regard myself as a woman who has seen much of life.” On February 3, 1889, two days before her 41st birthday, she was killed. She was riding home from a neighbor’s house in Eufaula, Oklahoma, when she was ambushed. After she fell off her horse, she was shot again to make sure she was dead. Her death resulted from shotgun wounds to the  back and neck and in the shoulder and face. Legend says she was shot with her own double barrel shotgun. According to Frank “Pistol Pete” Eaton, her death was due to different circumstances. She had been attending a dance. Frank Eaton had been the last person to dance with Belle Starr when Edgar Watson, clearly intoxicated had asked to dance with her. When Belle Starr declined, he later followed her. When on the way home, she stopped to give her horse a drink at a creek, he shot and killed her. According to Frank Eaton, Watson was tried, convicted and executed by hanging for the murder.
back and neck and in the shoulder and face. Legend says she was shot with her own double barrel shotgun. According to Frank “Pistol Pete” Eaton, her death was due to different circumstances. She had been attending a dance. Frank Eaton had been the last person to dance with Belle Starr when Edgar Watson, clearly intoxicated had asked to dance with her. When Belle Starr declined, he later followed her. When on the way home, she stopped to give her horse a drink at a creek, he shot and killed her. According to Frank Eaton, Watson was tried, convicted and executed by hanging for the murder.
Belle’s children didn’t do much better, and turned out as one would expect, with the influence their mother had on them. Belle’s son, Eddie Reed, was convicted of horse theft and receiving stolen property in July 1889. Judge Parker sent him to prison in Columbus, Ohio. Belle’s daughter, Rosie Reed, also known as Pearl Starr, became a prostitute to raise funds for Eddie’s release. She did eventually obtain a presidential pardon in 1893. Ironically, Eddie became a deputy in Fort Smith and killed two outlaw brothers named Crittenden in 1895, and was himself killed in a saloon in Claremore, Oklahoma on December 14, 1896. Pearl operated several brothels in Van Buren and Fort Smith, Arkansas, from the 1890s to World War I.
 As people prepare for Christmas, their days are busy shopping for gifts, and buying things for Christmas dinner. Their minds are on friends, family, and the coming holiday…not disaster. On December 23, 1982, disaster came in the form of a chemical…dioxin, which had been sprayed on the unpaved roads in the town of Times Beach, Missouri. On the 23rd, just two days before Christmas the Missouri Department of Health and the federal Centers for Disease Control (CDC) informed the residents that their town would have to be evacuated. They were told that not only would their town have to be evacuated, but it would also have to be demolished. It was a nightmare Christmas for the people of the town of about 2,000 people. These were their homes, and now the government was telling them that they had to leave. Sure they were offered money, and a chance to relocate somewhere, but some of the residents had lived there all their lives. They just didn’t want to leave. Some refused to sell. By February, the federal and state governments had spent $36 million to buy every house in town except one. Eventually, in 1985, there was only one couple left living in the town, George and Lorene Klein. People magazine profiled their last stand. “They wanted more money,” Leistner says. “She still blames me. I didn’t set the price, but it’s my fault. She doesn’t speak to me.” In 1985, the city was officially disincorporated.
As people prepare for Christmas, their days are busy shopping for gifts, and buying things for Christmas dinner. Their minds are on friends, family, and the coming holiday…not disaster. On December 23, 1982, disaster came in the form of a chemical…dioxin, which had been sprayed on the unpaved roads in the town of Times Beach, Missouri. On the 23rd, just two days before Christmas the Missouri Department of Health and the federal Centers for Disease Control (CDC) informed the residents that their town would have to be evacuated. They were told that not only would their town have to be evacuated, but it would also have to be demolished. It was a nightmare Christmas for the people of the town of about 2,000 people. These were their homes, and now the government was telling them that they had to leave. Sure they were offered money, and a chance to relocate somewhere, but some of the residents had lived there all their lives. They just didn’t want to leave. Some refused to sell. By February, the federal and state governments had spent $36 million to buy every house in town except one. Eventually, in 1985, there was only one couple left living in the town, George and Lorene Klein. People magazine profiled their last stand. “They wanted more money,” Leistner says. “She still blames me. I didn’t set the price, but it’s my fault. She doesn’t speak to me.” In 1985, the city was officially disincorporated.
Originally founded in 1925, Times Beach was actually part of a newspaper promotion: A 6-month subscription  to The St. Louis Times plus an extra $67.50 bought a 20-by-100–foot lot along an unsettled stretch of the Meramec River. The town never became the booming resort that the newspaper had intended it to be, but rather, it evolved into a lower-middle–class hamlet of about 2,000 people. It was located just off Route 66, the now famous two lane highway that ran from Chicago to Los Angeles, and was once was one of the major routes across the American Southwest. Unfortunately, being the small town that it was, Times Beach never had the money to pave its roads, and all the dust that was kicked up by vehicles was a real nuisance. In 1972, town officials thought they’d found a perfect solution to the problem: they paid local waste-hauler Russell Bliss just 6 cents per gallon to spray its roads with oil. The plan was to basically glue the dust to the ground, but we all know about the best laid plans. They had hoped the oil mixture would mix with the dirt and somehow glue it down. They never anticipated the problem the “cheaper solution” would cause.
to The St. Louis Times plus an extra $67.50 bought a 20-by-100–foot lot along an unsettled stretch of the Meramec River. The town never became the booming resort that the newspaper had intended it to be, but rather, it evolved into a lower-middle–class hamlet of about 2,000 people. It was located just off Route 66, the now famous two lane highway that ran from Chicago to Los Angeles, and was once was one of the major routes across the American Southwest. Unfortunately, being the small town that it was, Times Beach never had the money to pave its roads, and all the dust that was kicked up by vehicles was a real nuisance. In 1972, town officials thought they’d found a perfect solution to the problem: they paid local waste-hauler Russell Bliss just 6 cents per gallon to spray its roads with oil. The plan was to basically glue the dust to the ground, but we all know about the best laid plans. They had hoped the oil mixture would mix with the dirt and somehow glue it down. They never anticipated the problem the “cheaper solution” would cause.
Bliss got the oil for free the year before, when a chemical manufacturer that had made most of its money selling napalm to the military paid him to get rid of its waste materials. He mixed six truckloads of that waste…which turned out to be hexachlorophene tainted with dioxin, a dangerous chemical that, once absorbed, can remain in the human body for more than 10 years–with a tankful of used motor oil. Next, he sprayed this carcinogenic cocktail all over town. The children of Times Beach loved sliding around in Bliss’ purple-tinted goo,  and no one gave the substance a second thought until animals…particularly horses, who had contact with Bliss-sprayed roads and barn floors and riding rings every day, all year round…started dropping dead. Soon people started to get sick, too. In 1979, the EPA came to town and took soil samples, and in 1982 the agency announced that the levels of dioxin, “the most potent cancer-causing agent made by man,” in Times Beach were off the charts. The agency evacuated the town just after Christmas. In all, the agency spent $250 million and incinerated 265,000 tons of dioxin-tainted soil. In 1999, the bulldozed and cleaned-up Times Beach reopened as the Route 66 State Park. Times Beach has remained a Ghost Town since that time.
and no one gave the substance a second thought until animals…particularly horses, who had contact with Bliss-sprayed roads and barn floors and riding rings every day, all year round…started dropping dead. Soon people started to get sick, too. In 1979, the EPA came to town and took soil samples, and in 1982 the agency announced that the levels of dioxin, “the most potent cancer-causing agent made by man,” in Times Beach were off the charts. The agency evacuated the town just after Christmas. In all, the agency spent $250 million and incinerated 265,000 tons of dioxin-tainted soil. In 1999, the bulldozed and cleaned-up Times Beach reopened as the Route 66 State Park. Times Beach has remained a Ghost Town since that time.
 I think that were it not for the danger involved, I could be a storm chaser. I love to watch the shows about storm chasers and about tornadoes themselves. I suppose the main reason I like those shows is that you can watch the awesomeness of nature’s storms, but you don’t really have to deal with the reality of the loss of life and damage to property. It seems more like a scene from a movie. Nevertheless, the reality is that in a real storm situation, tornadoes kill and they damage property. The first recognized storm chaser was David Hoadley, who began chasing North Dakota storms in 1956. Hoadley used data from area weather offices and airports to calculate the possible areas for tornadic activity. Hoadley is considered the pioneer storm chaser and was the founder of Storm Track magazine. With storms such as the Tri-State Tornado which occurred on this day, March 18, 1925, and many others that followed, I’m sure that Hoadley could see that there was a need for someone to find a way to predict the path of these deadly storms.
I think that were it not for the danger involved, I could be a storm chaser. I love to watch the shows about storm chasers and about tornadoes themselves. I suppose the main reason I like those shows is that you can watch the awesomeness of nature’s storms, but you don’t really have to deal with the reality of the loss of life and damage to property. It seems more like a scene from a movie. Nevertheless, the reality is that in a real storm situation, tornadoes kill and they damage property. The first recognized storm chaser was David Hoadley, who began chasing North Dakota storms in 1956. Hoadley used data from area weather offices and airports to calculate the possible areas for tornadic activity. Hoadley is considered the pioneer storm chaser and was the founder of Storm Track magazine. With storms such as the Tri-State Tornado which occurred on this day, March 18, 1925, and many others that followed, I’m sure that Hoadley could see that there was a need for someone to find a way to predict the path of these deadly storms.
The March 18, 1925 tornado traveled across the tri-state area of eastern Missouri, southern Illinois, and southern Indiana, killing 695 people, injuring some 13,000 people, and causing $17 million in property damage. It became known as the Tri-State Tornado, and it shocked the nation. The tornado first touched down in Ellington, Missouri at about 1:00pm, but the worst hit area was southern Illinois. More than 500 of the 695 people lost dies in Illinois, including 234 in the city of Murphysboro and 127 in West Frankfort.
In all, the Tri-State Tornado traveled 219 miles in it’s path of destruction, and was on the ground more than three hours. It ripped through 164 square miles and was more than a mile wide. It traveled at speeds of more than 70 miles per hour. There has never been a worse tornado in the history of the United States. Years after the Tri-State Tornado, scientists discovered the cyclic nature of tornado-producing thunderstorms. These  storms are able to produce one tornado after another, in a seemingly continuous damage path, that could easily be mistaken for a single tornado, when they were actually a family of tornadoes. Of course, with all the time that had passed, and the lack of things like Doppler Radar to see what the storm really was, it is nearly impossible to determine 91 years later whether or not the Tri-State tornado was one or a family of tornadoes, it remains in the history books as the longest-tracked and deadliest single tornado in recorded history. I have to wonder if David Hoadley, or someone like him had been able to predict these storms, maybe the loss of life would have been much lower.
storms are able to produce one tornado after another, in a seemingly continuous damage path, that could easily be mistaken for a single tornado, when they were actually a family of tornadoes. Of course, with all the time that had passed, and the lack of things like Doppler Radar to see what the storm really was, it is nearly impossible to determine 91 years later whether or not the Tri-State tornado was one or a family of tornadoes, it remains in the history books as the longest-tracked and deadliest single tornado in recorded history. I have to wonder if David Hoadley, or someone like him had been able to predict these storms, maybe the loss of life would have been much lower.
 When a young woman gets married, she expects to live happily ever after. Unfortunately, for my husband, Bob Schulenberg’s second great grandmother, Mary LuLu Taylor, that was not to be. Mary, who went by LuLu, married Bob’s second great grandfather, James Leary on September 30, 1880 in Shelby, Missouri. They were very much in love. The young couple would move to Forsyth, Montana and on January 4, 1886, she gave birth to Bob’s great grandfather, Marion Chester Leary, who went by Chester for most of his life. Now their family had entered the next phase. They were no longer a couple, but rather, a family…at least for a while. The couple would move again, this time to St Louis, Missouri. March 26, 1888 would find LuLu a widow, with a two year old son to raise…alone.
When a young woman gets married, she expects to live happily ever after. Unfortunately, for my husband, Bob Schulenberg’s second great grandmother, Mary LuLu Taylor, that was not to be. Mary, who went by LuLu, married Bob’s second great grandfather, James Leary on September 30, 1880 in Shelby, Missouri. They were very much in love. The young couple would move to Forsyth, Montana and on January 4, 1886, she gave birth to Bob’s great grandfather, Marion Chester Leary, who went by Chester for most of his life. Now their family had entered the next phase. They were no longer a couple, but rather, a family…at least for a while. The couple would move again, this time to St Louis, Missouri. March 26, 1888 would find LuLu a widow, with a two year old son to raise…alone.
For a young mother in the 1880s, being a widow didn’t leave her with a lot of options. LuLu moved back to Shelby, where she met her second husband, James Begier. They  were married on March 18, 1890. LuLu thought her life had turned around, and in many ways, she was right. LuLu and James Begier went on to have Minnie in 1893, John in 1896, and Mable in 1902. I’m sure that by 1902, LuLu felt like her life was finally perfect. She had her husband and her children. Nevertheless, life would not reamin so perfect forever. This marriage would not be a happily ever after marriage either, because while James Begier’s death date is not known at this time, the last known census showing James Begier was in 1910.
were married on March 18, 1890. LuLu thought her life had turned around, and in many ways, she was right. LuLu and James Begier went on to have Minnie in 1893, John in 1896, and Mable in 1902. I’m sure that by 1902, LuLu felt like her life was finally perfect. She had her husband and her children. Nevertheless, life would not reamin so perfect forever. This marriage would not be a happily ever after marriage either, because while James Begier’s death date is not known at this time, the last known census showing James Begier was in 1910.
LuLu would remarry again on February 19, 1919 in Rosebud, Montana to Milo Warren. She had moved back to Forsyth because her eldest son, Chester Leary, was living there, with his family. When a woman is widowed, it is often the best option to move to where family lives…especially in those days. As with LuLu’s previous husbands, Milo would predecease her on August 21, 1928. Once again, LuLu moved. This time to be near her youngest daughter, Mabel Begier Brown. I don’t really know if Mabel was sick during this time or not, but LuLu passed away on April 26, 1929 in Fletcher, Oklahoma, and her daughter, Mabel Begier Brown passed away on  April 2, 1931 in Elgin, Oklahoma, and the young age of only 28 years.
April 2, 1931 in Elgin, Oklahoma, and the young age of only 28 years.
While, LuLu’s life was filled with times of sadness, she did nevertheless, live a full life. She had the opportunity to live in several places, and she was blessed with four children, and many grandchildren and multiple levels of great grandchildren, including my husband and his siblings, by daughters and their cousins, and my grandchildren and their cousins. While I never had the opportunity to meet LuLu in person, I have long beed intrigued by her life. My only regret is that I don’t have pictures of all her husbands…just James Begier, nor of her children…just Chester Leary. Nevertheless, I feel blessed to have those few. LuLu was born on August 31, 1861, and today is the 154th anniversary of her birth. Happy birthday in Heaven Mary LuLu Taylor Leary Begier Warren. I look forward to meeting you someday.
 With this year marking the 155th anniversary of the Pony Express, there is much celebration in the arena of those who love to celebrate the history of the Pony Express. Every year the first couple of weeks in June find many riders marking the amazing accomplishments of the Pony Express by riding the route once again. The riders follow the original route from Saint Louis, Missouri to Sacramento, California. They travel on horseback, just as the original riders did, and they ride 24 hours a day, just as the riders before them. Today, June 20, 2015 puts them traveling through the state of Wyoming. They left Atlantic City, Wyoming June 20, 3:00am, Farson, Wyoming at 9:00am, Green River Crossing at 11:00am, Granger, Wyoming at 12:30pm, Uinta County Line at 1:00pm, Fort Bridger, Wyoming at 4:00pm, and cross the Wyoming/Utah state line at 9:00pm, arriving in This Is The Place Heritage Park in Utah in time to depart on Sunday, June 21, 3:30am, to continue on to their destination of Sacramento, California with a planned arrival at Old Sacramento, California on Thursday, June 25, 11:30am.
With this year marking the 155th anniversary of the Pony Express, there is much celebration in the arena of those who love to celebrate the history of the Pony Express. Every year the first couple of weeks in June find many riders marking the amazing accomplishments of the Pony Express by riding the route once again. The riders follow the original route from Saint Louis, Missouri to Sacramento, California. They travel on horseback, just as the original riders did, and they ride 24 hours a day, just as the riders before them. Today, June 20, 2015 puts them traveling through the state of Wyoming. They left Atlantic City, Wyoming June 20, 3:00am, Farson, Wyoming at 9:00am, Green River Crossing at 11:00am, Granger, Wyoming at 12:30pm, Uinta County Line at 1:00pm, Fort Bridger, Wyoming at 4:00pm, and cross the Wyoming/Utah state line at 9:00pm, arriving in This Is The Place Heritage Park in Utah in time to depart on Sunday, June 21, 3:30am, to continue on to their destination of Sacramento, California with a planned arrival at Old Sacramento, California on Thursday, June 25, 11:30am.
The Pony Express is one of the few services that achieved so much recognition in such a short history. The service opened officially on April 3, 1860, when riders left simultaneously from St. Joseph, Missouri, and Sacramento, California. The first westbound trip was made in 9 days and 23 hours and the eastbound journey in 11 days and 12 hours. The pony riders covered 250 miles in a 24-hour day. Eventually, it gre to more than 100 stations, 80 riders, and 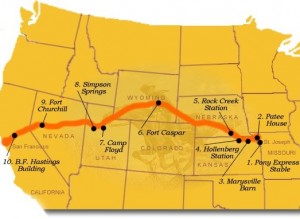 between 400 and 500 horses. Their delivery record was amazing in that during their run, only one mail delivery was lost. The service lasted only 19 months until October 24, 1861, when the completion of the Pacific Telegraph line ended the need for its existence.
between 400 and 500 horses. Their delivery record was amazing in that during their run, only one mail delivery was lost. The service lasted only 19 months until October 24, 1861, when the completion of the Pacific Telegraph line ended the need for its existence.
While it’s time was short, the Pony Exoress has become a beloved historic icon. In fact, in many ways, the service the Pony Express provided, makes our current mail service pale by comparison. I realize that there are many very good mail service workers, but there are also many who couldn’t care less about the mail they deliver, or the people sending or receiving it. They are, unfortunately, among the sorry generation of people who think a paycheck shouldn’t necessarily depend on the work performed, or not performed. That mentality was totally foreign to the Pony Express riders, who risked their very lives every day to make sure that communication in this great nation was possible. Happy 155th Anniversary to the Pony Express.

