immigrants
 America has been the land of opportunity since its inception, and people often worked years to save enough money to pay for passage to what many considered the promised land. It wasn’t cheap, but the money for passage was just the beginning of the grueling process of becoming a citizen of the United States. They knew some of what they would face, but not all. Still, it did not deter them. For a chance at a better life, they came. Many immigrants came through Ellis Island, passing by the Statue of Liberty on their way. It was their first glimpse of what they considered the symbol of America. Then they went on to Ellis Island, where their pre-entry screening began.
America has been the land of opportunity since its inception, and people often worked years to save enough money to pay for passage to what many considered the promised land. It wasn’t cheap, but the money for passage was just the beginning of the grueling process of becoming a citizen of the United States. They knew some of what they would face, but not all. Still, it did not deter them. For a chance at a better life, they came. Many immigrants came through Ellis Island, passing by the Statue of Liberty on their way. It was their first glimpse of what they considered the symbol of America. Then they went on to Ellis Island, where their pre-entry screening began.
First, they were rigorously questioned…what we call vetting today. They asked things like: “Are you meeting a relative here in America? Who? Have you been in a prison, almshouse, or institution for care of the insane? Are you a polygamist? Are you an anarchist? Are you coming to America for a job? Where will you work? Are you  deformed or crippled? Who was the first President of America? What is the Constitution? Which President freed the slaves? Can you name the 13 original Colonies? Who is the current President of the United States?” Providing they passed this first test, they moved on to the next level. Many people these days would take offense at some of these questions…especially the health questions. What they don’t understand is that an unhealthy person or one with a disability could have been a burden to society…even more so than the problems with disabilities today. I know that sounds bad, but they couldn’t afford to take lots of people that the government was going to have to support. They also couldn’t take people with a communicable disease that could cause an epidemic in our country…something we can all understand these days. Every immigrant with a medical condition was marked on their on the shoulder of their clothing with their condition. Things like “PG” for pregnant, “B” for back problems, “SC” for scalp condition, etc. That way, every station down the line knew the problem. Sick children had to be quarantined away from their parents.
deformed or crippled? Who was the first President of America? What is the Constitution? Which President freed the slaves? Can you name the 13 original Colonies? Who is the current President of the United States?” Providing they passed this first test, they moved on to the next level. Many people these days would take offense at some of these questions…especially the health questions. What they don’t understand is that an unhealthy person or one with a disability could have been a burden to society…even more so than the problems with disabilities today. I know that sounds bad, but they couldn’t afford to take lots of people that the government was going to have to support. They also couldn’t take people with a communicable disease that could cause an epidemic in our country…something we can all understand these days. Every immigrant with a medical condition was marked on their on the shoulder of their clothing with their condition. Things like “PG” for pregnant, “B” for back problems, “SC” for scalp condition, etc. That way, every station down the line knew the problem. Sick children had to be quarantined away from their parents.
Sometimes people had to be held at Ellis Island for a time…weeks and even months, until they got well, or could get someone who would agree to sponsor them with their disabilities. That said, another problem or set of problems occurred. There were minimal beds available at any given time, and people spoke different languages, making communication difficult. Often, fights broke out and had to be settled, and sometimes  people had to sleep on the floor. Sometimes, children came over alone. Their parents were dead, and they were sent to live with relatives or maybe to be adopted. Sometimes they were on Ellis Island for months…so long in fact that a playground was build so they could play. A school was started because they needed an education. And sometimes children had to be sent back alone or with a parent if they had one. Some people were rejected. It was part of the process. It was hard…on everyone, but the reward was a better life, if they were accepted. It was tough, and still, they came. They knew it was worth it. The nation has always accepted immigrants. We just expect them to do so legally. The process is difficult, but it is worth it.
people had to sleep on the floor. Sometimes, children came over alone. Their parents were dead, and they were sent to live with relatives or maybe to be adopted. Sometimes they were on Ellis Island for months…so long in fact that a playground was build so they could play. A school was started because they needed an education. And sometimes children had to be sent back alone or with a parent if they had one. Some people were rejected. It was part of the process. It was hard…on everyone, but the reward was a better life, if they were accepted. It was tough, and still, they came. They knew it was worth it. The nation has always accepted immigrants. We just expect them to do so legally. The process is difficult, but it is worth it.
 When we think of movie stars, we seldom think of them as soldiers, even if they have played a soldier on television or the movies. Nevertheless, many have served. One of my favorite shows as a kid was McHale’s Navy. McHale was played by Ernest Borgnine, who was born Ermes Effron Borgnino on January 24, 1917, in Hamden, Connecticut. Borgnine was the son of Italian immigrants. His mother, Anna (née Boselli; 1894–c. 1949), was from Carpi, near Modena. His father Camillo Borgnino (1891–1975) was a native of Ottiglio near Alessandria.
When we think of movie stars, we seldom think of them as soldiers, even if they have played a soldier on television or the movies. Nevertheless, many have served. One of my favorite shows as a kid was McHale’s Navy. McHale was played by Ernest Borgnine, who was born Ermes Effron Borgnino on January 24, 1917, in Hamden, Connecticut. Borgnine was the son of Italian immigrants. His mother, Anna (née Boselli; 1894–c. 1949), was from Carpi, near Modena. His father Camillo Borgnino (1891–1975) was a native of Ottiglio near Alessandria.
Borgnine had a normal childhood, and after high school, he enlisted in the United States Navy in October 1935. He served aboard the destroyer/minesweeper USS Lamberton and was honorably discharged from the Navy in October 1941. Then, the  attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1942, changed many things. In January 1942, Borgnine re-enlisted in the Navy. During World War II, he patrolled the Atlantic Coast on an antisubmarine warfare ship, the USS Sylph. In September 1945, he was honorably discharged from the Navy. With the two stints, Borgnine served a total of almost ten years in the Navy and obtained the grade of gunner’s mate 1st class. His military awards include the Navy Good Conduct Medal, American Defense Service Medal with Fleet Clasp, American Campaign Medal with ?3?16″ bronze star, and the World War II Victory Medal. Who knew?
attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1942, changed many things. In January 1942, Borgnine re-enlisted in the Navy. During World War II, he patrolled the Atlantic Coast on an antisubmarine warfare ship, the USS Sylph. In September 1945, he was honorably discharged from the Navy. With the two stints, Borgnine served a total of almost ten years in the Navy and obtained the grade of gunner’s mate 1st class. His military awards include the Navy Good Conduct Medal, American Defense Service Medal with Fleet Clasp, American Campaign Medal with ?3?16″ bronze star, and the World War II Victory Medal. Who knew?
 To me, it seems like all this also prepared him for his most famous television show. As a veteran sailor, he knew how things were run on a ship. Of course, how much of his knowledge could be used on the show depends on the directors. If they had any good sense, they would have used his knowledge, and made the show more realistic. Still, as a kid, I doubt if I would know if it was realistic or not, and after all these years, I can’t say I would recall any of the details. Nor would I know if they were realistic or not. Nevertheless, I always liked the show, and I really liked Ernest Borgnine. I just never knew that he had been a sailor during World War II, or that he had played a part in locating and sinking submarines. I also didn’t realize that he enlisted not once, but twice, or that he served a total of ten years. Years later, on July 8, 2012, after many years as a successful actor, Ernest Borgnine died of kidney failure on July 8, 2012 at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, California. He was 95 years old.
To me, it seems like all this also prepared him for his most famous television show. As a veteran sailor, he knew how things were run on a ship. Of course, how much of his knowledge could be used on the show depends on the directors. If they had any good sense, they would have used his knowledge, and made the show more realistic. Still, as a kid, I doubt if I would know if it was realistic or not, and after all these years, I can’t say I would recall any of the details. Nor would I know if they were realistic or not. Nevertheless, I always liked the show, and I really liked Ernest Borgnine. I just never knew that he had been a sailor during World War II, or that he had played a part in locating and sinking submarines. I also didn’t realize that he enlisted not once, but twice, or that he served a total of ten years. Years later, on July 8, 2012, after many years as a successful actor, Ernest Borgnine died of kidney failure on July 8, 2012 at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, California. He was 95 years old.

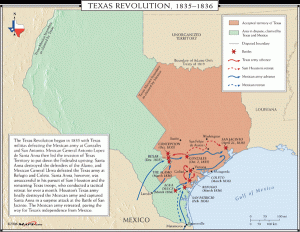 Since the 17th century, Texas, or Tejas as the Mexicans called it, had technically been a part of the Spanish empire. However, there were only about 3,000 Spanish-Mexican settlers in Texas, even as late as the 1820s, and Mexico City’s hold on the territory was very weak. Tensions were growing between Mexico and Texas, and on October 2, 1835, the area erupted into violence when Mexican soldiers attempted to disarm the people of Gonzales. People just don’t take kindly to having their guns taken away in any era, I guess. The citizens of Texas chose a war for independence of allowing the government to take their guns.
Since the 17th century, Texas, or Tejas as the Mexicans called it, had technically been a part of the Spanish empire. However, there were only about 3,000 Spanish-Mexican settlers in Texas, even as late as the 1820s, and Mexico City’s hold on the territory was very weak. Tensions were growing between Mexico and Texas, and on October 2, 1835, the area erupted into violence when Mexican soldiers attempted to disarm the people of Gonzales. People just don’t take kindly to having their guns taken away in any era, I guess. The citizens of Texas chose a war for independence of allowing the government to take their guns.
Mexico had just won it’s own independence from Spain in 1821. At this point, Mexico welcomed large numbers of Anglo-American immigrants into Texas. They were hoping that these citizens would become loyal Mexican citizens, thereby keeping the territory from falling into the hands of the United States. During the next decade men like Stephen Austin brought more than 25,000 people to Texas, most of them Americans. But while these emigrants legally became Mexican citizens, they continued to speak English, formed their own schools, and had closer trading ties to the United States than to Mexico.
The situation exacerbated in 1835, the president of Mexico, Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna, overthrew the constitution and appointed himself dictator. Recognizing that the “American” Texans were likely to use his rise to power as an excuse to secede, Santa Anna ordered the Mexican military to begin disarming the Texans whenever possible. He underestimated the people. His attempt to disarm proved more difficult than he could have ever imagined, and the situation exploded on that October day in 1835.
That day, the Mexican soldiers were attempting to take a small cannon from the village of Gonzales. To their surprise, they encountered much stiffer resistance than they ever thought possible from a hastily assembled militia of Texans. After a rather brief fight, the Mexicans retreated and the Texans kept their cannon. The determined Texans would continue to battle Santa Ana and his army for another year and a half before winning their independence and establishing the Republic of Texas. This truly goes to show that a nation, whose citizens are armed, is much more likely to be able to fend off their enemies…even if that enemy is a tyrannous government; than an nation of disarmed citizens. Yes, the ensuing war lasted for another year and a half, but 
 the people won their independence in the end. They later went on to become a part of the United States, and they continue to carry their guns to this day. The people of Texas are just as adamant about their right to bear arms today as they were in 1835, as are a good number of their fellow Americans. It’s a fight that would not likely be won by the government today either. The American people won’t accept the loss of guns without a fight of epic proportions!!
the people won their independence in the end. They later went on to become a part of the United States, and they continue to carry their guns to this day. The people of Texas are just as adamant about their right to bear arms today as they were in 1835, as are a good number of their fellow Americans. It’s a fight that would not likely be won by the government today either. The American people won’t accept the loss of guns without a fight of epic proportions!!
 My great grandparents, Carl and Henriette (Hensel) Schumacher immigrated to the United States from Germany, in 1884 and 1882 respectively. It was an amazing time for them. The United States was a whole new world, and for those who came, the land of opportunity. By 1886, they were married and ready to start a family. My grandmother, Anna Schumacher was born in 1887, followed by siblings Albert, Mary (who died before she was 3), Mina, Fred, Bertha, and Elsa, who was born in 1902.
My great grandparents, Carl and Henriette (Hensel) Schumacher immigrated to the United States from Germany, in 1884 and 1882 respectively. It was an amazing time for them. The United States was a whole new world, and for those who came, the land of opportunity. By 1886, they were married and ready to start a family. My grandmother, Anna Schumacher was born in 1887, followed by siblings Albert, Mary (who died before she was 3), Mina, Fred, Bertha, and Elsa, who was born in 1902.
By 1914, World War I broke out, following the assassination of Franz Ferdinand. The government of the United States was understandably nervous about the German immigrants now living in in America. It didn’t matter that many of these people had been living in the united States for a long time, and some had become citizens, married, and had families. The government was still nervous, and I can understand how that could be, because we have the same problem these days with the Muslim nations. Still, when I think about the fact that these were my sweet, kind, and loving, totally Lutheran great grandparents, I find it hard to believe that anyone could be nervous about them. Apparently, I was right, because to my knowledge, they were never detained in any of the internment camps, nor were they even threatened with it.
Nevertheless, there were German nationals, and even naturalized citizens who faced possible detention during 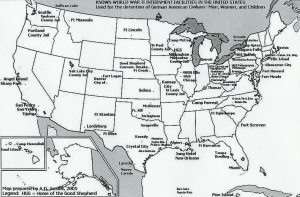 World War I and World War II. By World War II, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt declared Presidential Proclamation 2526, the legal basis for internment under the authority of the Alien and Sedition Acts. With the United States’ entry into World War I, the German nationals were automatically classified as “enemy aliens.” Two of the four main World War I-era internment camps were located in Hot Springs, North Carolina and Fort Oglethorpe, Georgia. Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer wrote that “All aliens interned by the government are regarded as enemies, and their property is treated accordingly.”
World War I and World War II. By World War II, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt declared Presidential Proclamation 2526, the legal basis for internment under the authority of the Alien and Sedition Acts. With the United States’ entry into World War I, the German nationals were automatically classified as “enemy aliens.” Two of the four main World War I-era internment camps were located in Hot Springs, North Carolina and Fort Oglethorpe, Georgia. Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer wrote that “All aliens interned by the government are regarded as enemies, and their property is treated accordingly.”
By the time of World War II, the United States had a large population of ethnic Germans. Among residents of the United States in 1940, more than 1.2 million persons had been born in Germany, 5 million had two native-German parents, and 6 million had one native-German parent. Many more had distant German ancestry. With that many people of German ancestry, it seems impossible that they could have detained all of them. Nevertheless, at least 11,000 ethnic Germans, overwhelmingly German nationals were detained during World War II in the United States. The government examined the cases of German nationals individually, and detained relatively few in internment camps run by the Department of Justice, as per its responsibilities under the Alien and Sedition Acts. To a much lesser extent, some ethnic German United States citizens were classified as suspect after due process and also detained. There were also a small proportion of Italian nationals  and Italian Americans who were interned in relation to their total population in the United States. The United States had allowed immigrants from both Germany and Italy to become naturalized citizens, which many had done by then. It was much less likely for those people to be detained, if they had already become citizens. In the early 21st century, Congress considered legislation to study treatment of European Americans during World War II, but it did not pass the House of Representatives. Activists and historians have identified certain injustices against these groups. I suppose that some injustices were done, but those were times of war and strong measures were needed.
and Italian Americans who were interned in relation to their total population in the United States. The United States had allowed immigrants from both Germany and Italy to become naturalized citizens, which many had done by then. It was much less likely for those people to be detained, if they had already become citizens. In the early 21st century, Congress considered legislation to study treatment of European Americans during World War II, but it did not pass the House of Representatives. Activists and historians have identified certain injustices against these groups. I suppose that some injustices were done, but those were times of war and strong measures were needed.
 You don’t grow up in central Wyoming without making at least one and more likely several trips to Independence Rock. It is a favorite for school field trips, and family outings as well…or at least it was when I was growing up. My family has climbed all over that rock looking at the names of the immigrants who passed by their on their way west. They would carve their name in the rock, as a way of saying, “I was here, in this place, on this date in history.” They had no way of knowing if anyone would ever see their name or care to wonder about who they were, but they wanted to mark their presence in time anyway. Lots of people have done that over the years, although these days people often use spray paint on the rocks or walls of a place, or even a sharp object on the stalls of a bathroom, which I have never been able to figure out. I mean, who cares about that. It’s just weird. Of course the difference is that the people who do that now are looked on with disdain, for defacing public property, but the immigrants heading to the old west were viewed as pioneers making their mark in history. I have to agree with that analogy, because graffiti is not like a historical record carved into a rock after all.
You don’t grow up in central Wyoming without making at least one and more likely several trips to Independence Rock. It is a favorite for school field trips, and family outings as well…or at least it was when I was growing up. My family has climbed all over that rock looking at the names of the immigrants who passed by their on their way west. They would carve their name in the rock, as a way of saying, “I was here, in this place, on this date in history.” They had no way of knowing if anyone would ever see their name or care to wonder about who they were, but they wanted to mark their presence in time anyway. Lots of people have done that over the years, although these days people often use spray paint on the rocks or walls of a place, or even a sharp object on the stalls of a bathroom, which I have never been able to figure out. I mean, who cares about that. It’s just weird. Of course the difference is that the people who do that now are looked on with disdain, for defacing public property, but the immigrants heading to the old west were viewed as pioneers making their mark in history. I have to agree with that analogy, because graffiti is not like a historical record carved into a rock after all.
Independence Rock is located in southwestern Natrona County along Highway 220, a little  over 55 miles from Casper, which is why many Casperites have been there so many times. It is a huge granite rock approximately 130 feet high, 1,900 feet long and 850 feet wide. It basically sticks up in the middle of an otherwise quite flat area on the prairie, with the mountains in the distance. I suppose that was why the pioneers decided to carve their names there. After a long day of travel, it was a good place to camp, with one side well protected and a great place to keep a watchful eye out for Indians or outlaws. The children could play on the rock, and that would put them out of their mothers’ hair while dinner was prepared. Some people say that it looks like a huge whale in the middle of the prairie, and I can say I must agree. Because of all the names carved in the rock, it was dubbed “Register of the Desert” by Peter DeSmet in 1840.
over 55 miles from Casper, which is why many Casperites have been there so many times. It is a huge granite rock approximately 130 feet high, 1,900 feet long and 850 feet wide. It basically sticks up in the middle of an otherwise quite flat area on the prairie, with the mountains in the distance. I suppose that was why the pioneers decided to carve their names there. After a long day of travel, it was a good place to camp, with one side well protected and a great place to keep a watchful eye out for Indians or outlaws. The children could play on the rock, and that would put them out of their mothers’ hair while dinner was prepared. Some people say that it looks like a huge whale in the middle of the prairie, and I can say I must agree. Because of all the names carved in the rock, it was dubbed “Register of the Desert” by Peter DeSmet in 1840.
Independence Rock was a favorite place to go rock hunting as far as my Grandpa George Byer was concerned, and the family went there quite a bit. It wasn’t a historical site then. Now, it is illegal to take rocks from that area, of course Grandpa would have never taken anything that had a name carved in it anyway. I’m sure that many of his kids have passed that tradition on to their kids, although, I don’t think many of the grandchildren take their kids there much anymore. It’s not that we wouldn’t think Independence Rock is interesting,  because I think many of us would, except that for a time you weren’t allowed to climb the rock to see the names recorded there. It was a little glitch in people’s thinking I think, and it made Independence Rock a lot less interesting to this generation. The time when climbing on the rock was prohibited came about because they didn’t want footsteps to kill the lichen, but I think they have changed that now, because the lichen was obscuring the names, and defacing the rock in it’s own way. I don’t go there much these days, but it will always hold a place in my memory files, because of all the fun we had there when Dad would take us to learn about history.
because I think many of us would, except that for a time you weren’t allowed to climb the rock to see the names recorded there. It was a little glitch in people’s thinking I think, and it made Independence Rock a lot less interesting to this generation. The time when climbing on the rock was prohibited came about because they didn’t want footsteps to kill the lichen, but I think they have changed that now, because the lichen was obscuring the names, and defacing the rock in it’s own way. I don’t go there much these days, but it will always hold a place in my memory files, because of all the fun we had there when Dad would take us to learn about history.![]()

