Politics

 Mikhail Tukhachevsky saw it coming, really. Sometimes it’s rather sad to be right about certain things. Tukhachevsky had been nicknamed the “Red Napoleon,” meaning that he was a popular Soviet military leader in Stalin’s Red Army. Tukhachevsky had no idea just how much more important the ideology would be to Stalin, than loyalty, ability, or anything else.
Mikhail Tukhachevsky saw it coming, really. Sometimes it’s rather sad to be right about certain things. Tukhachevsky had been nicknamed the “Red Napoleon,” meaning that he was a popular Soviet military leader in Stalin’s Red Army. Tukhachevsky had no idea just how much more important the ideology would be to Stalin, than loyalty, ability, or anything else.
After his service in World War I of 1914-1917 and in the Russian Civil War of 1917-1923, from 1920 to 1921 Tukhachevsky commanded the Soviet Western Front in the Polish–Soviet War. He was moving up the ranks, and with the Soviet forces under his command, he successfully repelled the Polish forces from Western Ukraine, driving them back into Poland. Nevertheless, the Red Army suffered defeat outside of Warsaw, and the war ended in a Soviet defeat.
Tukhachevsky went on to serve as chief of staff of the Red Army from 1925 through 1928, as assistant in the People’s Commissariat of Defense after 1934, and as commander of the Volga Military District in 1937. He achieved the rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union in 1935. Still, all of that did not protect him, in fact it put him in more danger, because he was just a little way under Stalin, and that was not going to bode well for him.
Tukhachevsky was arrested in 1936, suspected of being a German spy. The charges included Tukhachevsky’s supposed plot to overthrow Stalin. After he was arrested, the guards coerced a confession out of him. This was at the very beginning of The Great Terror, a term which historians have borrowed from the French Revolution. It refers to the paroxysm of state-organized bloodshed that overwhelmed the Communist Party and Soviet society during the years 1936-1938. It was also known as the Great Purges.
During this time, Stalin actually had over a million of his own soldiers killed for imagined wrongs. Stalin was, in  reality, half crazy. He was known to pluck a live chicken, just to see the reaction from his men. It wasn’t a really big stretch to move to killing soldiers or civilians, so the Great Terror wasn’t too far out there for him. As for Tukhachevsky, Stalin sentenced him to death in March 1938. He was executed on June 12, 1937. Even the men who had to judge the soldiers in those “sham” trials, were not free from danger. One of them, Ivan Belov said, “Tomorrow, I shall be put in the same place.” Belov was right. He was arrested on January 7, 1938. He was later executed as well. I can’t imagine how insane Stalin must have been. When you think about it, most of the men and women who were under Stalin’s rule, were too terrified to be disloyal.
reality, half crazy. He was known to pluck a live chicken, just to see the reaction from his men. It wasn’t a really big stretch to move to killing soldiers or civilians, so the Great Terror wasn’t too far out there for him. As for Tukhachevsky, Stalin sentenced him to death in March 1938. He was executed on June 12, 1937. Even the men who had to judge the soldiers in those “sham” trials, were not free from danger. One of them, Ivan Belov said, “Tomorrow, I shall be put in the same place.” Belov was right. He was arrested on January 7, 1938. He was later executed as well. I can’t imagine how insane Stalin must have been. When you think about it, most of the men and women who were under Stalin’s rule, were too terrified to be disloyal.
 His Elective Majesty…sounds almost laughable, but it was almost the proper way to address the President of the United States, a fact that some presidents would probably have liked very much. Some presidents have tried to “rule” as a king would have, so they figure, why not buy in whole heartedly. One such president, who in fact made the original suggestion of title, was none other than, at the time, Vice President John Adams. The idea came from the fact that other heads of state are known by honorifics such as “His Excellency” and such, but United States presidents are only ever Mr President…or “sir” in a pinch. I’m sure that John Adams already had his sights set on becoming president at some point, and the second president of the United States seemed as good a time to run as any…or maybe he liked his own idea very much.
His Elective Majesty…sounds almost laughable, but it was almost the proper way to address the President of the United States, a fact that some presidents would probably have liked very much. Some presidents have tried to “rule” as a king would have, so they figure, why not buy in whole heartedly. One such president, who in fact made the original suggestion of title, was none other than, at the time, Vice President John Adams. The idea came from the fact that other heads of state are known by honorifics such as “His Excellency” and such, but United States presidents are only ever Mr President…or “sir” in a pinch. I’m sure that John Adams already had his sights set on becoming president at some point, and the second president of the United States seemed as good a time to run as any…or maybe he liked his own idea very much.

Apparently, thinking that the office of the President of the United States needed a title with more grandeur, Adams suggested that a president should be referred to as either “His Elective Majesty,” “His Mightiness,” or the slightly excessive “His Highness, the President of the United States of America and the Protector of their Liberties.” Just imagine any of those ideas. Every one of them make me giggle. Just take a moment to say (out loud) those titles in connection with the president…any president. With some presidents, any one of these titles is hilarious, and I’ll let you to decide to whom that statement applies, because these days we all have very specific opinions on the matter.
In those days, Washington was very aware of public fear about their newly won democracy slipping back into a  monarchy. They didn’t want this new nation to be too similar to England. They didn’t want this newly free nation to become once again ruled by a different kind of monarchy. So, they refused to allow the president to be titled as anything other than “The President of the United States.” They were right, of course, because the United States is not a “spin-off” of England…like England 2.0. The United States is a very unique nation…unlike any other, before her or after her. This nation was founded by people who refused to be told what to believe anymore. That is why they left England, where they were forced to live under a “state religion.” The nation was founded as “one nation, under God.” We would not have a king, because Jesus was our King of kings. We couldn’t give that title to a mere man.
monarchy. They didn’t want this new nation to be too similar to England. They didn’t want this newly free nation to become once again ruled by a different kind of monarchy. So, they refused to allow the president to be titled as anything other than “The President of the United States.” They were right, of course, because the United States is not a “spin-off” of England…like England 2.0. The United States is a very unique nation…unlike any other, before her or after her. This nation was founded by people who refused to be told what to believe anymore. That is why they left England, where they were forced to live under a “state religion.” The nation was founded as “one nation, under God.” We would not have a king, because Jesus was our King of kings. We couldn’t give that title to a mere man.

 I have always known that I was stubborn, and “bull headed” and if you ask my sisters, they will very much agree with me on that fact, but I seriously doubt if they would ever call me stubborn if I were compared to President Theodore Roosevelt. I don’t think many people are as stubborn as Roosevelt was. Roosevelt didn’t run for his initial term in office, but rather became president of the United States because William McKinley was assassinated while Roosevelt was serving as vice president. He did run for and win a second term in the election of 1904, during which he promised not to run for a third term thereafter. A man of his word to a point, Roosevelt stuck to that promise through the 1908 election, but then he decided to run for President again in 1912, first losing the Republican primary to the incumbent William Taft and then running at the head of a brand-new party, the Progressive “Bull Moose” Party. It is a strange name for a political party, but I think it might have been appropriate for Roosevelt.
I have always known that I was stubborn, and “bull headed” and if you ask my sisters, they will very much agree with me on that fact, but I seriously doubt if they would ever call me stubborn if I were compared to President Theodore Roosevelt. I don’t think many people are as stubborn as Roosevelt was. Roosevelt didn’t run for his initial term in office, but rather became president of the United States because William McKinley was assassinated while Roosevelt was serving as vice president. He did run for and win a second term in the election of 1904, during which he promised not to run for a third term thereafter. A man of his word to a point, Roosevelt stuck to that promise through the 1908 election, but then he decided to run for President again in 1912, first losing the Republican primary to the incumbent William Taft and then running at the head of a brand-new party, the Progressive “Bull Moose” Party. It is a strange name for a political party, but I think it might have been appropriate for Roosevelt.
When Roosevelt decided to run for president again in 1912, a saloon owner named John Schrank became obsessed with him, and after having a nightmare that convinced Schrank that Roosevelt was responsible for McKinley’s assassination. That fueled his obsession, and on October 14, 1912, he walked up to Roosevelt as he exited a Milwaukee hotel on route to a campaign event and fired a .38-caliber revolver right into his chest. For most people, this would be the end of the story, but this is where Roosevelt really earned the name attached to the political party of which he was a member.
Unfortunately, Schrank was not a bad shot, and the bullet hit its mark. Fortunately, the path of the bullet was not an easy one. After passing through Roosevelt’s glasses case and 50 pages worth of notes in his breast pocket, which slowed it down considerably the bullet hit Roosevelt’s chest. The items in its way likely slowed the bullet enough to save Roosevelt’s life. Then, in typical “bull headed” fashion, the former president coughed into his hands to check for blood, and upon finding none, continued on to the Milwaukee Auditorium, where he delivered an 84-minute speech that began with the following lines, “Friends, I shall ask you to be as quiet as possible. I don’t know whether you fully understand that I have just been shot; but it takes more than that to kill a Bull Moose. But fortunately, I had my manuscript, so you see I was going to make a long speech, and there is a bullet – there is where the bullet went through – and it probably saved me from it going into my heart. The bullet is in me now, so that I cannot make a very long speech, but I will try my best.”
The bullet stayed lodged in his ribs throughout the rest of his unsuccessful campaign, and until his passing in 
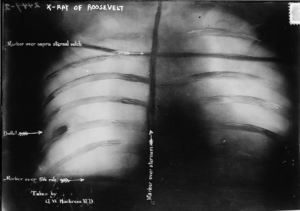 1919. While Roosevelt lost his race, his determination did show the kind of fortitude it takes to be president of this country. Being the leader of the free world, is not something that can be handled easily. The President of the United States must be an anointed position, and it is not one that just anyone can handle. In many ways, the best presidents are a type of “bull moose.” They have to be to take the pounding they have to take, and then keep coming back for more.
1919. While Roosevelt lost his race, his determination did show the kind of fortitude it takes to be president of this country. Being the leader of the free world, is not something that can be handled easily. The President of the United States must be an anointed position, and it is not one that just anyone can handle. In many ways, the best presidents are a type of “bull moose.” They have to be to take the pounding they have to take, and then keep coming back for more.
 During World War II, the Nazis had a little problem…the resistance. Of course, the resistance had to be very careful, and stay in hiding much of the time. There were informants, the police, and the enemy soldiers to watch out for. It was hard to tell sometimes who was an enemy and who was a friend. Every day was spent in hiding, and often in fear for their lives.
During World War II, the Nazis had a little problem…the resistance. Of course, the resistance had to be very careful, and stay in hiding much of the time. There were informants, the police, and the enemy soldiers to watch out for. It was hard to tell sometimes who was an enemy and who was a friend. Every day was spent in hiding, and often in fear for their lives.
With the Allied invasion of Normandy, the French resistance saw an opportunity to really increase their activity in the area. Of course, there were more fighter pilots in need of an escape routes, and soldiers who were wounded, but they also saw a way to strike back. One such way was to kidnap and kill Helmut Kampfe, a major in the Waffen-SS Das Reich. Of course, all resistance action came at a cost. Following the killing of Kampfe, a battalion of the regiment known  as Der Fuhrer Regiment was sent to the small village of Oradour-sur-Glane.
as Der Fuhrer Regiment was sent to the small village of Oradour-sur-Glane.
Of course, the village was innocent, but someone had to pay so Commander Adolf Diekmann ordered the town sealed off, the men locked in barns, and the women and children confined to the church. Nobody knows why the town was chosen for this attack. Maybe it was due to the town’s proximity to the regiment, or maybe it was because the Germans knew the village was defenseless. Whatever it was, it was about to get brutal.
Diekmann ordered his unit to begin shooting. It was like a terrorist attack. The residents were first incapacitated by gunshots to the legs. When they  were unable to move, the barns and church were doused with gasoline and ignited. Hundreds of the villagers died that day, nearly all the residents of the area. Many of the SS who were there that day were Alsatian French nationals who had been forced into the German military, and almost all them escaped punishment, which is a crime in itself. After World War II, French president Charles De Gaulle declared that the village was never to be restored. It was to stand as it was after the attack, as a reminder of the brutal Nazi occupation. Brutality like that should never be forgotten, and maybe the evidence should stand as a reminder of the evil that exists in some people. Lest we forget.
were unable to move, the barns and church were doused with gasoline and ignited. Hundreds of the villagers died that day, nearly all the residents of the area. Many of the SS who were there that day were Alsatian French nationals who had been forced into the German military, and almost all them escaped punishment, which is a crime in itself. After World War II, French president Charles De Gaulle declared that the village was never to be restored. It was to stand as it was after the attack, as a reminder of the brutal Nazi occupation. Brutality like that should never be forgotten, and maybe the evidence should stand as a reminder of the evil that exists in some people. Lest we forget.
 The hardest part about being a commander in any war situation is that moment when you have to tell a soldier’s family that they have been killed in action. It’s even easier to tell them that their soldier is missing, because at least then they have hope. The only thing that could possibly be harder than telling a soldiers family that they have been killed is to tell sibling soldiers’ family that they have been killed. That is the lot that fell to President Abraham Lincoln, according to legend, on November 21, 1864, except it came to him in spades. On that day, Lincoln composed a letter to Lydia Bixby, a widow and mother of five men, all of whom had been killed in the Civil War. It was a completely tragic state of affairs, and so made national news when a copy of the letter was published in the Boston Evening Transcript on November 25. It was signed by “Abraham Lincoln.” Oddly, the original letter has never been found, so it continues to be “legend” to this day.
The hardest part about being a commander in any war situation is that moment when you have to tell a soldier’s family that they have been killed in action. It’s even easier to tell them that their soldier is missing, because at least then they have hope. The only thing that could possibly be harder than telling a soldiers family that they have been killed is to tell sibling soldiers’ family that they have been killed. That is the lot that fell to President Abraham Lincoln, according to legend, on November 21, 1864, except it came to him in spades. On that day, Lincoln composed a letter to Lydia Bixby, a widow and mother of five men, all of whom had been killed in the Civil War. It was a completely tragic state of affairs, and so made national news when a copy of the letter was published in the Boston Evening Transcript on November 25. It was signed by “Abraham Lincoln.” Oddly, the original letter has never been found, so it continues to be “legend” to this day.
After expressing his condolences to Mrs Bixby on the death of her five sons, who had fought to preserve the Union in the Civil War, Lincoln goes on to express his regrets on how “weak and fruitless must be any words of mine which should attempt to beguile you from the grief of a loss so overwhelming.” He then continued with a prayer that “our Heavenly Father may assuage the anguish of your bereavement [and leave you] the cherished memory of the loved and lost, and the solemn pride that must be yours, to have laid so costly a sacrifice upon the altar of Freedom.”
Historians continue to debate the authorship of the letter, and the authenticity of copies printed between 1864 and 1891. Nevertheless, at that time, copies of presidential messages were often published and then sold as souvenirs. Many historians and archivists agree that the original letter was probably written by Lincoln’s secretary, John Hay. As to Mrs Bixby’s loss, scholars have since discovered that only two of her sons actually died fighting during the Civil War. A third was honorably discharged and a fourth was dishonorably thrown out of the Army. The fifth son’s fate is unknown, but it is assumed that he deserted or died in a Confederate prison camp. The facts in this case seem to show that sometimes Presidents are given misinformation, resulting in heartbreaking mistakes. If Mrs Bixby did receive this letter, it is my opinion that she quite likely fainted on the  spot, and then to find out later that the president had been given wrong information that caused him, gentle man that he was, to feel the need to write this particular letter himself, rather than letting the commanding officer be the bearer of such bad news.
spot, and then to find out later that the president had been given wrong information that caused him, gentle man that he was, to feel the need to write this particular letter himself, rather than letting the commanding officer be the bearer of such bad news.
I’m sure that upon finding that there had been an error, President Lincoln was appropriately appalled, but at that point there was not much to do about it. The letter had been sent, and to bring up the additional facts, especially the son that was thrown out of the army, would have only made matters worse. In addition, they did not know where the missing son was, and possibly didn’t know for sure where the others were either, so it made sense to leave well enough alone. Still, I’m sure their mother would like to have known where her sons really were. While this situation was possibly, or at least partially, an awful mistake, it is still the hardest part of the job of commander, and one that is usually felt very deeply by those who have had to write such a letter.
 It’s never a good idea to find your nation behind it’s enemies in the arms race. Never was that made more clear than during the Cold War. It’s also not a good idea to begin to brag to your enemies about the superiority of your nation over theirs concerning the nation’s arms race status. Nevertheless, in a long and rambling interview with an American reporter on November 15, 1957, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev claimed that the Soviet Union had missile superiority over the United States. He then went on to challenge America to a missile “shooting match” to prove his assertion. It was a bold move, and one that fueled fears in the United States that the nation was indeed falling behind the Soviets in the arms race. People began to worry about not only the idea of the United States falling behind in the arms race, but also the idea that the Soviet Union and Nikita Khrushchev might actually launch their missiles at the US.
It’s never a good idea to find your nation behind it’s enemies in the arms race. Never was that made more clear than during the Cold War. It’s also not a good idea to begin to brag to your enemies about the superiority of your nation over theirs concerning the nation’s arms race status. Nevertheless, in a long and rambling interview with an American reporter on November 15, 1957, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev claimed that the Soviet Union had missile superiority over the United States. He then went on to challenge America to a missile “shooting match” to prove his assertion. It was a bold move, and one that fueled fears in the United States that the nation was indeed falling behind the Soviets in the arms race. People began to worry about not only the idea of the United States falling behind in the arms race, but also the idea that the Soviet Union and Nikita Khrushchev might actually launch their missiles at the US.
Khrushchev tried to compare the arms race to the space race, saying that if the United States had intercontinental ballistic rockets, “she had would have launched her own Sputnik.” Khrushchev was crossing boastful belligerence and calls for “peaceful coexistence” with the West, in what was a classic move for him. He bragged about Soviet missile superiority, claiming that the United States did not have what the Soviet Union had. Then, as cool as a cucumber, he issued a challenge, saying, “Let’s have a peaceful rocket contest just like a rifle-shooting match, and they’ll see for themselves.”
Following his fear-inspiring statements, Khrushchev began to speak about the future of East-West relations, saying that the American and Soviet people both wanted peace. He cautioned that although the Soviet Union would never start a war, “some lunatics” might bring about a conflict. In particular, he noted that Secretary of State John Foster Dulles had created “an artificial war psychosis.” In the case of war, it “would be fought on the American continent, which can be reached by our rockets.” NATO forces in Europe would also be devastated, and Europe “might become a veritable cemetery.” While the Soviet Union would “suffer immensely,” the forces of communism would ultimately destroy capitalism.
Khrushchev made these remarks just a few days after the Gaither Report had been leaked to the press in the  United States. The report supported many of the Russian leader’s contentions, charging that the United States was falling far behind the Soviets in the arms race. Of course, the critics of President Dwight D Eisenhower’s foreign policy, especially the Democratic Party, went on the attack, calling Eisenhower weak. The Gaither Report called for “an urgent strengthening of US missile technology, along with offensive and defensive military capabilities. The report also called for a fifty percent increase in US military spending and a redesign of the US Defense Department.” The Gaither Report was presented to President Eisenhower on November 7, 1957. The report suggested that Eisenhower’s military policy…the reliance on cheap nuclear weapons instead of expensive Army divisions…was inadequate. He kept the Report secret and generally ignored it, but its conclusions were leaked to the press. The public debate concerning the alleged “missile gap” between US and Soviet rocket arsenals continued through the early 1960s and became a major issue in the 1960 presidential campaign between Richard Nixon and John F Kennedy.
United States. The report supported many of the Russian leader’s contentions, charging that the United States was falling far behind the Soviets in the arms race. Of course, the critics of President Dwight D Eisenhower’s foreign policy, especially the Democratic Party, went on the attack, calling Eisenhower weak. The Gaither Report called for “an urgent strengthening of US missile technology, along with offensive and defensive military capabilities. The report also called for a fifty percent increase in US military spending and a redesign of the US Defense Department.” The Gaither Report was presented to President Eisenhower on November 7, 1957. The report suggested that Eisenhower’s military policy…the reliance on cheap nuclear weapons instead of expensive Army divisions…was inadequate. He kept the Report secret and generally ignored it, but its conclusions were leaked to the press. The public debate concerning the alleged “missile gap” between US and Soviet rocket arsenals continued through the early 1960s and became a major issue in the 1960 presidential campaign between Richard Nixon and John F Kennedy.
 Those who support Socialism, Marxism, and Communism have simply never lived under these forms of government, or they are a part of the upper echelon of such a government. People who have been forced to live under these types of government, will ultimately try to find a way of escape or will participate in a national uprising, such as the one that happened in Hungary in 1956.
Those who support Socialism, Marxism, and Communism have simply never lived under these forms of government, or they are a part of the upper echelon of such a government. People who have been forced to live under these types of government, will ultimately try to find a way of escape or will participate in a national uprising, such as the one that happened in Hungary in 1956.
Sadly, by the time the people realize that they are in serious trouble, the government often has such a chokehold on the nation that the only way out if to have an uprising. Nevertheless, people will eventually fight for their rights, or fight to escape. While the uprising in Hungary began in October 1956, when thousands of protesters took to the streets demanding a more democratic political system and freedom from Soviet oppression, the real problem started long before that. It started when the Communist Party took over and began to systematically take away the rights of the people. There were a few people within the party who could see through the Communist Party’s ideas. When party officials appointed Imre Nagy, a former premier who had been dismissed from the party for his criticisms of Stalinist policies, as the new premier, he began to try to restore peace and asked the Soviets to withdraw their troops. The Soviets did so, but Nagy then tried to push the Hungarian revolt forward by abolishing one-party rule. He also announced that Hungary was withdrawing from the Warsaw Pact (the Soviet bloc’s equivalent of NATO).
This forced the hand of the Soviet government. On November 4, 1956, Soviet tanks rolled into Budapest to  crush the national uprising, once and for all. Te fighting in the streets was vicious, but the Soviets’ greater power ensured their victory. The people had long been stripped of their weapons, and anything else that might have helped the achieve victory. At 5:20am Hungarian Prime Minister Imre Nagy announced the invasion to the nation in a grim, 35-second broadcast, declaring: “Our troops are fighting. The Government is in place.” He tried to reassure the people and keep hope alive, but within hours, Nagy sought asylum at the Yugoslav Embassy in Budapest. He was captured shortly thereafter and executed two years later. Nagy’s former colleague and imminent replacement, János Kádár, who had been flown secretly from Moscow to the city of Szolnok, 60 miles southeast of the capital, prepared to take power with Moscow’s backing. The conspiracy was complete, and the people had been betrayed…even their leader.
crush the national uprising, once and for all. Te fighting in the streets was vicious, but the Soviets’ greater power ensured their victory. The people had long been stripped of their weapons, and anything else that might have helped the achieve victory. At 5:20am Hungarian Prime Minister Imre Nagy announced the invasion to the nation in a grim, 35-second broadcast, declaring: “Our troops are fighting. The Government is in place.” He tried to reassure the people and keep hope alive, but within hours, Nagy sought asylum at the Yugoslav Embassy in Budapest. He was captured shortly thereafter and executed two years later. Nagy’s former colleague and imminent replacement, János Kádár, who had been flown secretly from Moscow to the city of Szolnok, 60 miles southeast of the capital, prepared to take power with Moscow’s backing. The conspiracy was complete, and the people had been betrayed…even their leader.
The people of the West were stunned by the Soviet action. Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev had promised to retreat from the Stalinist policies and repression of the past, but the violent actions in Budapest told of a different plan. An out of control government will always chose its own greedy ways over the good of the people it is supposed to serve. On that day, an estimated 2,500 Hungarians died and 200,000 more fled as refugees. Sporadic armed resistance, strikes, and mass arrests continued for months thereafter, causing substantial economic disruption. The spontaneous national uprising that began 12 days before in Hungary was viciously crushed by Soviet tanks and troops on November 4, 1956.

Many Hungarians were angered and frustrated by the inaction on the part of the United States. Voice of America radio broadcasts and speeches by President Dwight D Eisenhower and Secretary of State John Foster Dulles had recently suggested that the United States supported the “liberation” of “captive peoples” in communist nations, but they didn’t see that playing out in their situation. During that time, approximately 30,000 Hungarian refugees were allowed to enter the United States. Yet, as Soviet tanks bore down on the protesters, the United States did nothing beyond issuing public statements of sympathy for their plight.
 Politics is always a dirty game. That is probably why most of us don’t like career politicians. They will do or say anything to win or further their careers. “Dirty politics” has been around as long as there have been politicians…and politics isn’t even limited to just politicians. There’s office politics, military politics, law enforcement politics, and more.
Politics is always a dirty game. That is probably why most of us don’t like career politicians. They will do or say anything to win or further their careers. “Dirty politics” has been around as long as there have been politicians…and politics isn’t even limited to just politicians. There’s office politics, military politics, law enforcement politics, and more.
General George Washington wasn’t even exempt. In October 1777, while serving as the commander of the Continental Army, Washington was informed of a conspiracy to discredit him with Congress and have him replaced by General Horatio Gates. The loosely organized attempt was supposedly led by Brigadier General Thomas Conway, who was an Irish member of the French army. Conway commanded a brigade in Washington’s army, and he was unhappy with Washington’s performance in the Battle of Brandywine. Conway was also bragging about his own feats at the same operation. Conway was even so bold as to request a promotion for himself, to the rank of major general…based on the merits of his “performance” in the battle. Washington protested Conway’s promotion and was irritated by the request, believing it would have disastrous effects on the morale of more senior officers. I think the biggest problem was the arrogance of Conway. It just isn’t right to brag on yourslf so much.
Thomas Conway, would be made inspector general of the United States less than two months later on December 14, but it is my belief that it was in an effort to pigeon-hole hime, because he was an embarrassment. Conway, was born in Ireland, but raised in France. He entered the French army in 1749. Silas Deane, the American ambassador to France, recruited Conway to the Patriot cause. Conway met with Washington at Morristown in May 1777, after which, he was appointed brigadier general and assigned to Major General John Sullivan’s division. Conway served admirably under Sullivan at the battles of Brandywine, in September 1777, and Germantown, in October 1777, before becoming involved in an unconfirmed conspiracy to remove General Washington from command of the Continental Army. It ruined his military career.

Conway wasn’t alone in the cabal. The Continental Army had suffered several defeats in the fall of 1777, and some members of Congress felt it was Washington’s leadership that was to blame. Conway began writing letters to prominent leaders, including General Horatio Gates, that were critical of Washington. After Washington got wind of Conway’s letter to General Gates, he wrote his own letter to Congress in January 1778. Conway was embarrassed, and in March 1778, he offered his resignation as an apology. Nevertheless, he was surprised and humiliated when Congress accepted. After General John Cadwalader wounded him in a duel defending Washington’s honor, Conway returned to France, where he died in exile in 1800…unable to recover his dignity after the horrific Conway Cabal.
 For a number of years Israel had no place to call home. That sounds like a strange thing, but for the nation of Israel, it was not a new thing. Biblical history tells us of a number of times that Israel’s God-given land was taken from them for a time, and they were taken into captivity. Even after the captivity the Jewish people were displaced from their promised land. They were also persecuted and subject to racial discrimination.
For a number of years Israel had no place to call home. That sounds like a strange thing, but for the nation of Israel, it was not a new thing. Biblical history tells us of a number of times that Israel’s God-given land was taken from them for a time, and they were taken into captivity. Even after the captivity the Jewish people were displaced from their promised land. They were also persecuted and subject to racial discrimination.
That began to change when on November 2, 1917, Foreign Secretary Arthur James Balfour wrote an important letter to Britain’s most illustrious Jewish citizen, Baron Lionel Walter Rothschild, expressing the British government’s support for a Jewish homeland in Palestine. I can only imagine how the Baron felt. This was like having someone offer you the moon. It was something the Jew never thought they would see again. Many didn’t think they would live long enough to see it. The letter would eventually become known as the Balfour Declaration, and it was the start of something good.
Because of concerns over the direction World War I was going, the British were very supportive of the Zionist movement. Lloyd George among others, held a genuine belief in the righteousness of Zionism, but Britain’s leaders also hoped that a statement supporting Zionism would help gain Jewish support for the Allies. On November 2, Balfour sent his letter to Baron Rothschild, who was a prominent Zionist and a friend of Chaim Weizmann, stating that: “His Majesty’s Government view with favor the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people.”
The influence of the Balfour Declaration on the course of post-war events was immediate: According to the “mandate” system created by the Versailles Treaty of 1919, Britain was entrusted with the administration of Palestine, with the understanding that it would work on behalf of both its Jewish and Arab inhabitants. In 1948, the Balfour Declaration was scheduled to expire and Great Britain would no longer rule Palestine. The future of the Jewish people was at stake. The question over what to do with the  turbulent country was turned over to the United Nations. They, at the insistence of President Harry Truman, eventually decided to create the new country of Israel, specifically as a promised homeland for Jewish people. The new country was to be located across the various holy locations in which many events of the Old Testament occurred. The Jewish people were back in the promised land.
turbulent country was turned over to the United Nations. They, at the insistence of President Harry Truman, eventually decided to create the new country of Israel, specifically as a promised homeland for Jewish people. The new country was to be located across the various holy locations in which many events of the Old Testament occurred. The Jewish people were back in the promised land.
That was when United States President Harry Truman became the first world leader to officially recognize Israel as a legitimate Jewish state. On May 14, 1948, only eleven minutes after its creation the decree was delivered. His decision came after much discussion and advice from the White House staff, all of whom had differing viewpoints. Some advisors felt that creating a Jewish state was the only proper response to the Holocaust and would benefit American interests. Others took the opposite view, concerned about that the creation of a Jewish state would create more conflict in an already tumultuous region. No matter what happens, it was the right thing to do.
 When the minerals in a mine run out, or become less valuable, the mine tends to close down. These days, they try to return the mine to it’s prior state, but then many mines these days are pit mines, or strip mines. I suppose it is easier to return them to their prior state when you only have to fill in the hole, and I’m not opposed to that process. It can make a beautiful place out of ground that has been ripped apart. In some cases, it looks better after the reclamation.
When the minerals in a mine run out, or become less valuable, the mine tends to close down. These days, they try to return the mine to it’s prior state, but then many mines these days are pit mines, or strip mines. I suppose it is easier to return them to their prior state when you only have to fill in the hole, and I’m not opposed to that process. It can make a beautiful place out of ground that has been ripped apart. In some cases, it looks better after the reclamation.
The Kennecott Mine, often spelled Kennicott, is an abandoned mining camp in the Valdez-Cordova Census Area, which is now the Copper River Census Area in the state of Alaska. The mine was, at one time, the center of activity for several copper mines. Kennecott Mines was named after the Kennicott Glacier in the valley below. The geologist Oscar Rohn named the glacier after Robert Kennicott during the 1899 US Army Abercrombie Survey. A “clerical error” resulted in the substitution of an “e” for the “i,” supposedly by Stephen Birch himself. The mine is located northeast of Valdez, inside Wrangell-Saint Elias National Park and Preserve. The camp and mines are now a National Historic Landmark District administered by the National Park Service. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1986. It’s status as a historical site, probably explains the good shape it is in. Many historical sites deteriorate badly before anyone realizes that they should be preserved as a part of history.
Two prospectors, “Tarantula” Jack Smith and Clarence L Warner, who were with a group of prospectors associated with the McClellan party in the summer of 1900, spotted “a green patch far above them in an  improbable location for a grass-green meadow.” Upon inspection, the green turned out to be malachite, located with chalcocite…aka “copper glance,” and the location of the Bonanza claim. A few days later, Arthur Coe Spencer, US Geological Survey geologist also found chalcocite at the same location. It was the birth of a copper mine.
improbable location for a grass-green meadow.” Upon inspection, the green turned out to be malachite, located with chalcocite…aka “copper glance,” and the location of the Bonanza claim. A few days later, Arthur Coe Spencer, US Geological Survey geologist also found chalcocite at the same location. It was the birth of a copper mine.
A mining engineer just out of school, named Stephen Birch was in Alaska looking for investment opportunities in minerals. He was young, but he came with the financial backing of the Havemeyer Family and another investor named James Ralph, from his days in New York. Birch spent the winter of 1901-1902 acquiring the “McClellan group’s interests” for the Alaska Copper Company of Birch, Havemeyer, Ralph and Schultz, later to become the Alaska Copper and Coal Company. He spent the summer of 1901, visiting the property and “spent months mapping and sampling.” He confirmed the Bonanza mine and surrounding deposits, were at the time, the richest known concentration of copper in the world.
Kennecott had five mines: Bonanza, Jumbo, Mother Lode, Erie, and Glacier. “Glacier, which is really an ore extension of the Bonanza, was an open-pit mine and was only mined during the summer. Bonanza and Jumbo were on Bonanza Ridge about 3 miles from Kennecott. The Mother Lode mine was located on the east side of the ridge from Kennecott. The Bonanza, Jumbo, Mother Lode and Erie mines were connected by tunnels. The Erie mine was perched on the northwest end of Bonanza Ridge overlooking Root Glacier about 3.7 miles up a glacial trail from Kennecott.” The copper ore was transported to Kennecott by way of the trams which head-ended at Bonanza and Jumbo. From Kennecott the ore was hauled mostly in 140-pound sacks on steel flat cars  to Cordova, 196 rail miles away on the Copper River and Northwestern Railway (CRNW).
to Cordova, 196 rail miles away on the Copper River and Northwestern Railway (CRNW).
In 1925 a Kennecott geologist predicted that the end of the high-grade ore bodies was in sight. The mines days were numbered. The highest grades of ore were largely depleted by the early 1930s. The Glacier Mine closed in 1929, and the rest followed soon after. The last train left Kennecott on November 10, 1938. It was now a ghost town. Over a period of 20 years the population dropped from 494 in 1920 to 5 in 1940. Thankfully the historical value of this particular site was not lost, and is still there today.

