History

 One of the most unique buildings in the United States is the Pentagon. I’m sure that most people think that it was built the way it was to provide a better level of security for the people working within its walls, but that was not the case at all.
One of the most unique buildings in the United States is the Pentagon. I’m sure that most people think that it was built the way it was to provide a better level of security for the people working within its walls, but that was not the case at all.
The Pentagon was originally planned for a different location, but for reasons unknow, the structure could not be built on that location. The original location was a rather tight space, so in an effort to fit the building in the field that was located between five major roads, the design of an irregular pentagon was chosen. The building couldn’t be very tall due to regulations in the area, and so  the design was an almost-level irregular pentagon. Still, the building needed to house 40,000 people and have parking for 10,000 vehicles. That is a very tall order, for a short building. In the end, the planned location, was not allowed, and the Pentagon had to be moved.
the design was an almost-level irregular pentagon. Still, the building needed to house 40,000 people and have parking for 10,000 vehicles. That is a very tall order, for a short building. In the end, the planned location, was not allowed, and the Pentagon had to be moved.
Of course, with the location change, it was thought, at first, that the design to be changed too, but everyone involved in the design immediately got mad about the change. The designer had already been paid for his work, and it wasn’t really fair to take the payment back, nor did they want to pay for something they did not use. Finally it was decided to go ahead with the original design, and the result is the well-known, irregular pentagon shape that we are all very familiar with. While the Pentagon is synonymous world-wide with defense, he design had nothing to do with defense at all, but rather it was in an effort to put the building in the space allowed…much like a child putting a square peg in a square hole so that it fits.

 The White Rose was a non-violent, intellectual resistance group in the Third Reich led by a group of students including Hans and Sophie Scholl. The students attended the University of Munich. Their goal was to promote awareness using an anonymous leaflets and a graffiti campaign that called for active opposition to the Nazi regime. Of course, while the actions were anonymous, the Third Reich had spies everywhere. The activities of The White Rose started in Munich on June 27, 1942, and ended with the arrest of the core group by the Gestapo on February 18, 1943. The core group, as well as other members and supporters of the group who carried on distributing the pamphlets, were sentenced to death or imprisonment in show trials by the Nazi People’s Court (Volksgerichtshof).
The White Rose was a non-violent, intellectual resistance group in the Third Reich led by a group of students including Hans and Sophie Scholl. The students attended the University of Munich. Their goal was to promote awareness using an anonymous leaflets and a graffiti campaign that called for active opposition to the Nazi regime. Of course, while the actions were anonymous, the Third Reich had spies everywhere. The activities of The White Rose started in Munich on June 27, 1942, and ended with the arrest of the core group by the Gestapo on February 18, 1943. The core group, as well as other members and supporters of the group who carried on distributing the pamphlets, were sentenced to death or imprisonment in show trials by the Nazi People’s Court (Volksgerichtshof).
Hans and Sophie Scholl and Christoph Probst were among the members of the core group. They were captured on February 18, 1943. During the trial, Sophie interrupted the judge multiple times, but she was ignored. No defendants were given any opportunity to speak. They had no way to defend themselves, and were found guilty at the “trial.” They were executed by guillotine four days after their arrest, on February 22, 1943. The group had only been active for eight months, they had never committed a violent act, and yet they were put to death. Hitler’s regime considered them more of a threat for pamphlets and paintings, than if the had run around shooting people.
The group wrote, printed, and initially distributed their pamphlets in the greater Munich region. As the movement grew, secret carriers brought copies to other cities, mostly in the southern parts of Germany. The White Rose authored a total of six leaflets, which were multiplied and spread. In all, about 15,000 copies were printed. They denounced the Nazi regime’s crimes and oppression, and called for resistance. They openly 
 denounced the persecution and mass murder of the Jews, in their second leaflet. By the time of their arrest, the members of the White Rose were just about to establish contacts with other German resistance groups like the Kreisau Circle or the Schulze-Boysen/Harnack group of the Red Orchestra. Today, the White Rose is well known both within Germany and worldwide. Sadly the movement ended almost before it could get started.
denounced the persecution and mass murder of the Jews, in their second leaflet. By the time of their arrest, the members of the White Rose were just about to establish contacts with other German resistance groups like the Kreisau Circle or the Schulze-Boysen/Harnack group of the Red Orchestra. Today, the White Rose is well known both within Germany and worldwide. Sadly the movement ended almost before it could get started.

 With each new story of disaster, pandemic, or even murderous scare tactics, the news media splashes the newspaper, internet, and television with sensationalistic stories of doom and gloom. Yes, these things are serious matters, but sometimes I wonder if the news media are the only ones who are doing well throughout the crisis. It’s not that the news media doesn’t have a job to do so that the people are well informed, but even the doctors are saying that they have far overdone the current news stories. The news media has led people to believe that this is going to get so bad that entire cities are going to be quarantined for extended periods of time. The news reports are so bad, that it has prompted people to run out and buy up every necessity to the point of shortages. Things like toilet paper, hand sanitizer, face masks, disinfecting wipes, and rubbing alcohol are in seriously short supply. People are buying far more than they could possibly us in more than a year. There have even been people who won’t drink Carona beer, because of the similarity to the name of the virus. The insanity is astounding!!
With each new story of disaster, pandemic, or even murderous scare tactics, the news media splashes the newspaper, internet, and television with sensationalistic stories of doom and gloom. Yes, these things are serious matters, but sometimes I wonder if the news media are the only ones who are doing well throughout the crisis. It’s not that the news media doesn’t have a job to do so that the people are well informed, but even the doctors are saying that they have far overdone the current news stories. The news media has led people to believe that this is going to get so bad that entire cities are going to be quarantined for extended periods of time. The news reports are so bad, that it has prompted people to run out and buy up every necessity to the point of shortages. Things like toilet paper, hand sanitizer, face masks, disinfecting wipes, and rubbing alcohol are in seriously short supply. People are buying far more than they could possibly us in more than a year. There have even been people who won’t drink Carona beer, because of the similarity to the name of the virus. The insanity is astounding!!
I’m not saying that people don’t need to know about the situation, but when you turn on the news and all you hear is the fear mongering of the news media. The drama seekers need to set aside the need to “make their entire career” with the latest crisis, and instead give the information needed, in a clear non-dramatic manner so people have the ability to make sensible decisions about their own health. The way the latest media-managed crisis is being handled is like yelling “fire” in a packed event center. Yes, you’ll clear the place out, but lives will be lost in the process.
For some time now, the news media has been throwing out so much fake news that people no longer believe the news media. That is a dangerous place to be, because, like the boy who cried “wolf,” after a while nobody is listening anymore. They already know that the news media is just sensationalizing the story, so it’s probably all a lie anyway. If there ever is a serious crisis, it will arrive before anyone can prepare, because the screaming of the news media into the wind, is no longer being heard. It’s time for the news media to get back to the 
 “honorable,” “fair and balanced,” “we report, you decide” way of reporting again, so they can begin to rebuild the people’s trust, which they lost long ago. Since the news media can’t stop the sensationalism, it’s time for the people to use common sense, and show that we are wiser than the news media. There are so many ways to protect ourselves, without mass hysteria.
“honorable,” “fair and balanced,” “we report, you decide” way of reporting again, so they can begin to rebuild the people’s trust, which they lost long ago. Since the news media can’t stop the sensationalism, it’s time for the people to use common sense, and show that we are wiser than the news media. There are so many ways to protect ourselves, without mass hysteria.
 As the Allies were planning the massive D-Day assault which was intended to end World War II in Europe, some strange “coincidences” happened that almost threw a monkey wrench into the whole thing. The planned assault on Normandy, France, in 1944, was to include over 5,000 ships, 1,200 planes, and almost 160,000 men. They were set to invade Europe from the British Isles, when something almost put a stop to it…a series of crossword puzzles. Personally, I hate crossword puzzles. They are boring in my mind, so if I were to find a clue in one, it would likely be a miracle.
As the Allies were planning the massive D-Day assault which was intended to end World War II in Europe, some strange “coincidences” happened that almost threw a monkey wrench into the whole thing. The planned assault on Normandy, France, in 1944, was to include over 5,000 ships, 1,200 planes, and almost 160,000 men. They were set to invade Europe from the British Isles, when something almost put a stop to it…a series of crossword puzzles. Personally, I hate crossword puzzles. They are boring in my mind, so if I were to find a clue in one, it would likely be a miracle.
The problem began with the Dieppe Raid on August 19th, 1942. Dieppe is also in Normandy, but further North. In Dieppe, over 6,000 Allied troops, mostly from Canada, attacked at 5 AM. “They had four main goals: (1) to prove that it was possible to capture a slice of Nazi-occupied Europe, (2) to boost Allied morale, (3) to gain intelligence, and (4) to destroy coastal defenses and other sensitive installations.” The mission failed miserably, with the loss of, capture of, or retreat of almost 60% of the invading forces by 3 PM. This couldn’t have been just coincidental, and the Allies wanted to know what had happened. It seemed quite likely that the Germans had been warned of the attack. How could this have happened. Somehow, the suspicion fell on The Daily Telegraph, a British paper still in business today. I’m sure there were a number of newspapers over the years that were used to pass coded messages to the enemy. And I guess it would take a spy’s mind to figure it all out. It had to be discreet, because the paper can’t just give advance warning notice to the enemy, but they did (and still do) have a crossword puzzle section. What better avenue for coded messages. The thing that really triggered suspicion was that two days before the Dieppe invasion, the clue, “French port” was given. And the solution was “Dieppe,” given the following day…the day before the invasion. When I think about the 6,000 men that walked into an ambush because of that one puzzle, I feel furious. This wasn’t a coincidence, this was deliberate, and it was criminal.
The intelligence personnel quickly focused on Leonard Sydney Dawe…the headmaster of Strand School, who was responsible for the crossword puzzle. They were surprised to think it might be him, because he was a veteran of World War I. In addition, nothing linked him to Nazi Germany. In the end, MI5 concluded that it was just that a chilling coincidence, but was it…really? The Strand School for boys in south London, which no longer exists, still stuck out as being somehow involved. It was learned that when the Germans began their bombardment of the city in 1939, Strand was moved to Effingham in Surrey, which was close to where many American and Canadian forces were based.
The French invasion was called Operation Overlord. It was to take place on June 5th, 1944 and involve a series of joint sea and air landings along the Normandy coast. Rather than mass themselves at one spot, however, they were to land at five different areas according to nationality. The Americans were to land at two places. The first was on the left bank of the Douve estuary…codenamed Utah Beach. The second was the stretch which included Sainte-Honorine-des-Pertes, Saint-Laurent-sur-Mer, and Vierville-sur-Mer…referred to as Omaha. The  British were also given two landing sites – the first along Saint-Aubin-sur-Mer to Ouistreham…Sword Beach, as well as the strip from Arromanches-Les-Bains, Le Hamel, and La Rivière…Gold Beach. As for the Canadians, they were assigned the stretch from Courseulles, Saint-Aubin, and Bernières…Juno Beach. To ensure the quick off-loading of cargo, portable bridges called “Mulberry Harbors” were built. Ships would tow these to France, assemble them at sea, then drive equipment onto the beaches.
British were also given two landing sites – the first along Saint-Aubin-sur-Mer to Ouistreham…Sword Beach, as well as the strip from Arromanches-Les-Bains, Le Hamel, and La Rivière…Gold Beach. As for the Canadians, they were assigned the stretch from Courseulles, Saint-Aubin, and Bernières…Juno Beach. To ensure the quick off-loading of cargo, portable bridges called “Mulberry Harbors” were built. Ships would tow these to France, assemble them at sea, then drive equipment onto the beaches.
The massive size of the invasion, made it almost impossible to keep a complete secret from the Germans, so the plan was to keep them guessing as to exactly when and where the invasion would take place. It was then that the Allies launched Operation Bodyguard…a series of diversions which convinced the Germans that Normandy was simply a distraction, while the main invasion was to take place elsewhere. The Germans bought it, they didn’t want to take any chances. As a result, they stretched their forces thin in a desperate attempt to cover all of their bases. To keep them off balance, absolute secrecy was vital.
Then, in February 1944, one of The Daily Telegraph’s crossword answers was “JUNO.” The following month, it was “GOLD,” and the month after that, it was “SWORD.” Coincidence? MI5 thought so. Then, when the next puzzle included the clue, “One of the US,” they began to wonder. The next day, the answer given was “UTAH.” This was really too much, and MI5 was getting worried. As soon as the May 22nd edition came out, MI5 anxiously grabbed a copy. Scanning the crossword section, they found yet another suspicious clue…“Red Indian on the Missouri River.” And what was the answer given the next day? “OMAHA.” Lets just say, they were getting nervous. Still, it got worse. The May 27th edition had another damning clue…“Big-Wig.” And the answer was? “OVERLORD.” The clincher came on June 1…four days before lift-off. The solution to 15 Down was “NEPTUNE.”
Dawe was arrested at his school to the astonishment of the students and staff. They then banned the paper’s next publication in case “DDAY” appeared in the next crossword. The US Coast Guard manned USS LST-21 unloads British Army tanks and trucks onto a “Rhino” barge during the early hours of the invasion on Gold Beach, 6 June 1944. Dawe was released after the invasion but refused to speak about his ordeal till 1958. He admitted that they did turn him “inside-out,” and had D-Day turned into another Dieppe, he might have been shot. Many people thought it was all just a coincidence…at least till 1984 when Ronald French, a former student at Strand, came forward. As it turns out, Dawe didn’t create crossword puzzles. He instead had students arrange words on a grid, and when he was satisfied, provided clues to solve them by. Then he’d send the finished work to the paper, taking credit for the work. According to French and other former students who later came forward, everyone in Surrey knew the code words. It seems that because they all hung around the Americans and Canadians, the words had leaked out. The French didn’t know what the words meant, only that the servicemen often said them. So when told to work on the crossword puzzles, he included the codes. After his release, Dawes confronted French and accused him of putting the entire country at risk, but how had this 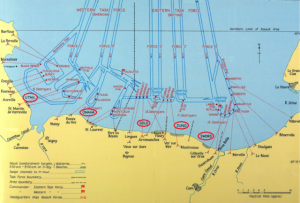 happened. It seems that despite their own secrecy, the MI5 had apparently forgotten to tell the army to keep their mouths shut. It all came about because when the Allies believed that the war was turning in their favor, the Third Washington Conference…also called the Trident Conference…was held in Washington, DC in May 1943. It was there that plans for an Allied invasion of Sicily, France, and the Pacific were discussed. The careless soldiers that spilled the code words almost cost the Allies the victory. D-Day was a battle that cost the Allies many lives, but it could have been much worse, if the secrets had been passed to the enemy in a way that they could have understood them.
happened. It seems that despite their own secrecy, the MI5 had apparently forgotten to tell the army to keep their mouths shut. It all came about because when the Allies believed that the war was turning in their favor, the Third Washington Conference…also called the Trident Conference…was held in Washington, DC in May 1943. It was there that plans for an Allied invasion of Sicily, France, and the Pacific were discussed. The careless soldiers that spilled the code words almost cost the Allies the victory. D-Day was a battle that cost the Allies many lives, but it could have been much worse, if the secrets had been passed to the enemy in a way that they could have understood them.
 When I think of some of the civilian heroes of our wars, I find myself amazed at the many courageous acts they carried out. They threw caution to the wind and moved about among the enemy, somehow managing to remain almost invisible. They had code names and secret pasts that no one knew about, not even the people they worked with…and definitely not the enemy they worked against.
When I think of some of the civilian heroes of our wars, I find myself amazed at the many courageous acts they carried out. They threw caution to the wind and moved about among the enemy, somehow managing to remain almost invisible. They had code names and secret pasts that no one knew about, not even the people they worked with…and definitely not the enemy they worked against.
One of these spies was Nancy Grace Augusta Wake, who was also known by her married name, Nancy Fiocca. Wake was a New Zealand-born nurse and journalist, who joined the French Resistance and later the Special Operations Executive (SOE) during World War II. Born August 30, 1912 in Roseneath, Wellington, New Zealand, the youngest of the six children of Charles Augustus Wake and Ella Rosieur Wake. In 1914, the family moved to Australia and settled at North Sydney. Shortly thereafter, Wake’s father returned to New Zealand and her mother raised the children. In Sydney, Wake attended the North Sydney Household Arts (Home Science) School.
At the age of 16, she ran away from home and worked as a nurse. With £200 (about $255.27) that she had inherited from an aunt, she traveled to New York City, then London where she trained herself as a journalist. In the 1930s, she worked in Paris and later for Hearst newspapers as a European correspondent. She witnessed the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi movement and “saw roving Nazi gangs randomly beating Jewish men and women in the streets” of Vienna. The Nazi movement repulsed her.
In 1937, Wake met wealthy French industrialist Henri Edmond Fiocca, whom she married on November 30, 1939. They were living in Marseille, France when Germany invaded. During the war in France, Wake served as an ambulance driver. After the fall of France in 1940, she joined the French Resistance, working in the escape network of Captain Ian Garrow, which became the Pat O’Leary Line. Wake had an incredible ability to elude capture, which earned her the nickname, “White Mouse” by the Gestapo. The Resistance exercised caution with her missions, because her life was in constant danger. The Gestapo tapped her telephone and intercepted her mail. In spite of the danger, Wake said, “I don’t see why we women should just wave our men a proud goodbye and then knit them balaclavas.” As a member of the escape network, she helped Allied airmen evade capture by the Germans and escape to neutral Spain.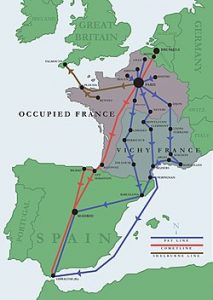
In November 1942, Wehrmacht troops occupied the southern part of France after the Allies’ Operation Torch had started. This gave the Germans and the Gestapo unrestricted access to all parts of Vichy France and made life more dangerous for Wake. When the network was betrayed that same year she decided to flee France. Her husband, Henri Fiocca, stayed behind. He later was captured, tortured, and executed by the Gestapo. She threw caution to the wind. She would “doll” herself up and be very flirtatious, almost daring them to search her. She took a chance, and they couldn’t see past her façade to the ruthless spy beneath the beauty she showed on the outside.
In 1943, when the Germans became aware of her, she escaped to Spain and continued on to the United Kingdom. After reaching Britain, Wake joined the Special Operations Executive (SOE) under the code name Hélène. On April 29-30, 1944 as a member of a three person SOE team code-named “Freelance,” Wake parachuted into the Allier department of occupied France to liaise between the SOE and several Maquis groups in the Auvergne region, which were loosely overseen by Emile Coulaudon (code name “Gaspard”). She participated in a battle between the Maquis and a large German force in June 1944. In the aftermath of the battle, she bicycled 500 kilometers to send a situation report to SOE in London. In early 1943, in the process of getting out of France, Wake was picked up with a whole trainload of people and was arrested in Toulouse, but was released four days later. The head of the O’Leary Line, Albert Guérisse, managed to have her released by claiming she was his mistress and was trying to conceal her infidelity to her husband (all of which was untrue). She succeeded in crossing the Pyrenees to Spain. Until the war ended, she was unaware of her husband’s death, and she subsequently blamed herself for it. Wake was a recipient of the George Medal from the United Kingdom, the Medal of Freedom from the United States, the Legion of Honor from France, and medals from Australia and New Zealand.
In 1985, Wake published her autobiography, “The White Mouse.” Later, after 40 years of marriage, her second husband John Forward died at Port Macquarie on 19 August 1997. The couple had no children. Wake sold her medals to fund herself saying, “There was no point in keeping them, I’ll probably go to hell and they’d melt anyway.” Strangely, this disregard of the value of war medals, seemed common among the war spies. In 2001, Wake left Australia for the last time and emigrated to London. She became a resident at the Stafford Hotel in Saint James’ Place, near Piccadilly, formerly a British and American forces club during the war. She had been introduced to her first “bloody good drink” there by Louis Burdet, the general manager at the time, who had  also worked for the Resistance in Marseille. Mornings usually found Wake in the hotel bar, sipping her first gin and tonic of the day. She was welcomed at the hotel, celebrating her ninetieth birthday there. Out of deep respect for her, the hotel owners absorbed most of the costs of her stay. In 2003, Wake chose to move to the Royal Star and Garter Home for Disabled Ex-Service Men and Women, in Richmond, London, where she remained until her death on Sunday evening August 7, 2011, aged 98, at Kingston Hospital, where she had been admitted with a chest infection. She had requested that her ashes be scattered at Montluçon in central France. Her ashes were scattered near the village of Verneix, which is near Montluçon, on March 11, 2013.
also worked for the Resistance in Marseille. Mornings usually found Wake in the hotel bar, sipping her first gin and tonic of the day. She was welcomed at the hotel, celebrating her ninetieth birthday there. Out of deep respect for her, the hotel owners absorbed most of the costs of her stay. In 2003, Wake chose to move to the Royal Star and Garter Home for Disabled Ex-Service Men and Women, in Richmond, London, where she remained until her death on Sunday evening August 7, 2011, aged 98, at Kingston Hospital, where she had been admitted with a chest infection. She had requested that her ashes be scattered at Montluçon in central France. Her ashes were scattered near the village of Verneix, which is near Montluçon, on March 11, 2013.
 Lyudmila Mikhailivna Pavlichenko was a Soviet sniper in the Red Army during World War II, credited with 309 confirmed kills. Her record made her the most successful female sniper in history. Lyudmila was nicknamed “Lady Death” due to her incredible ability with a sniper rifle and her high kill count. She served in the Red Army during the Siege of Odessa and the Siege of Sevastopol, during the early stages of the Eastern Front in World War II. Born Lyudmila Mikhailovna Belova on July 12, 1916 in Bila Tserkva, Russian Empire (located within present-day Ukraine). Her mother was a teacher and her father was a Saint Petersburg factory worker.
Lyudmila Mikhailivna Pavlichenko was a Soviet sniper in the Red Army during World War II, credited with 309 confirmed kills. Her record made her the most successful female sniper in history. Lyudmila was nicknamed “Lady Death” due to her incredible ability with a sniper rifle and her high kill count. She served in the Red Army during the Siege of Odessa and the Siege of Sevastopol, during the early stages of the Eastern Front in World War II. Born Lyudmila Mikhailovna Belova on July 12, 1916 in Bila Tserkva, Russian Empire (located within present-day Ukraine). Her mother was a teacher and her father was a Saint Petersburg factory worker.
In June 1941, when Pavlichenko was 24 years old and in her fourth year studying history at Kiev University, Germany began its invasion of the Soviet Union. Pavlichenko was among the first round of volunteers at the Odessa recruiting office, where she requested to join the infantry. The registrar really wanted her to be a nurse, but she refused. She surprised her superiors, and after they saw that she had completed multiple training courses, they finally let her in the army as a sniper. Pavlichenko was assigned to the Red Army’s 25th Rifle Division. She became one of 2,000 female snipers in the Red Army. The number sounds large, but female soldiers were still just 2% of the Red Army’s total number. Of the 2,000 female snipers, only about 500 survived the war. Pavlichenko was given only a frag grenade due to weapon shortages, although she was in a combat role. On August 8, 1941 a fallen comrade handed her his Mosin-Nagant model 1891 bolt-action rifle. She finally had a real weapon, and with it she achieved her first two kills and proved herself to her comrades. She described this event that made her officially a sniper, her “baptism of fire.”
Pavlichenko fought for about two and a half months near Odessa, where she recorded 187 kills. She was promoted to Senior Sergeant in August 1941, when she reached 100 confirmed kills. At age 25, she married a fellow sniper whose name was Alexei Kitsenko. Unfortunately, soon after the marriage, Alexei was gravely wounded by a mortar shell. He died from his injuries after a few days in the hospital. When the Romanians gained control of Odessa on October 15, 1941, Pavlichenko’s unit was withdrawn by sea to Sevastopol on the Crimean Peninsula, where she fought for more than eight months. In Sevastopol, Pavlichenko trained almost a dozen snipers, who killed over a hundred Axis soldiers during the battle. In May 1942, newly promoted Lieutenant Pavlichenko was cited by the Southern Army Council for killing 257 Axis soldiers. Her total of confirmed kills during World War II was 309, including 36 enemy snipers. In June 1942, Pavlichenko was hit in the face with shrapnel from a mortar shell. After her injury, the Soviet High Command ordered that she be evacuated from Sevastopol by submarine. They didn’t want to lose this valuable, perfect example of Soviet womanhood. She spent around a month in the hospital, after which she expected to go back to the Eastern Front , but she didn’t. Instead she became a propagandist for the Red Army. She also trained snipers for combat duty till the end of the war in 1945.
In 1942, Pavlichenko was sent to Canada and the United States for a publicity visit. Her mission was to convince the allies to start a second front against Nazi Germany. When she visited the United States, she became the first Soviet citizen to be received by a US President, as Franklin D. Roosevelt welcomed her to the White House, and later she toured with Eleanor Roosevelt across America, relating her experiences as a female soldier on the front lines. Unfortunately, Pavlichenko was not taken seriously by the press during her tour, but was referred to as the “Girl Sniper.” I can’t imagine how the press could possibly connect a sniper with girlish innocence. She was dumbfounded by the kind of questions reporters put to her in Washington, DC. “One reporter even criticized the length of the skirt of my uniform, saying that in America women wear shorter skirts and besides my uniform made me look fat.” They also asked if she used makeup on the front line. She was described by the reporters as very blunt and unemotional in her responses. Pavlichenko appeared before the International Student Assembly being held in Washington, DC, attended the meetings of the Congress of Industrial Organizations, and made appearances and speeches in New York City and Chicago. In New York City, she was given a raccoon fur coat by Mayor LaGuardia. In Chicago, she stood before large crowds, chiding the men to support the second front. “Gentlemen,” she said, “I am 25 years old and I have killed 309 fascist invaders by now. Don’t you think, gentlemen, that you have been hiding behind my back for too long?” Her words settled on the crowd, then caused a surging roar of support.
 On Friday, November 12, 1942, Pavlichenko visited Coventry, accepting donations of £4,516 from local workers to pay for three X-ray units for the Red Army. She also visited Coventry Cathedral ruins, then the Alfred Herbert works and Standard Motor Factory, from where most funds had been raised. She had inspected a factory in Birmingham earlier in the day. Having attained the rank of major, Pavlichenko never returned to combat, but became an instructor and trained Soviet snipers until the war’s end. In 1943, she was awarded the Gold Star of the Hero of the Soviet Union, as well as the Order of Lenin twice. Lyudmilla Pavlichenko died on October 10, 1974, at the age of 58 years in Moscow, Soviet Union due to a stroke. She was a beloved hero of the Soviet Union.
On Friday, November 12, 1942, Pavlichenko visited Coventry, accepting donations of £4,516 from local workers to pay for three X-ray units for the Red Army. She also visited Coventry Cathedral ruins, then the Alfred Herbert works and Standard Motor Factory, from where most funds had been raised. She had inspected a factory in Birmingham earlier in the day. Having attained the rank of major, Pavlichenko never returned to combat, but became an instructor and trained Soviet snipers until the war’s end. In 1943, she was awarded the Gold Star of the Hero of the Soviet Union, as well as the Order of Lenin twice. Lyudmilla Pavlichenko died on October 10, 1974, at the age of 58 years in Moscow, Soviet Union due to a stroke. She was a beloved hero of the Soviet Union.
 Recently I read a novel that was based on a true story, called “The Alice Network,” by Kate Quinn. Knowing the book was a novel, I assumed that it was entirely fictional, but then I began to wonder, so I researched “The Alice Network” for myself. I found that “The Alice Network” was a very much true story, even if some of the characters in the story were fictional. The head of the Alice Network, Louise Marie Jeanne Henriette de Bettignies, was very much a real person.
Recently I read a novel that was based on a true story, called “The Alice Network,” by Kate Quinn. Knowing the book was a novel, I assumed that it was entirely fictional, but then I began to wonder, so I researched “The Alice Network” for myself. I found that “The Alice Network” was a very much true story, even if some of the characters in the story were fictional. The head of the Alice Network, Louise Marie Jeanne Henriette de Bettignies, was very much a real person.
Louise Marie Jeanne Henriette de Bettignies was born on July 15, 1880 to Henri de Bettignies and Julienne Mabille de Poncheville. She was fluent in French and English, with a good mastery in German and Italian. It made her a perfect candidate for the spy network. Louise became a French secret agent who spied on the Germans for the British during World War I using the pseudonym of Alice Dubois, hence “The Alice Network.” She had under her direction, a number of men and women who mainly worked in the area of Lille, in German occupied France. Her people listened inconspicuously to the talk of the German soldiers when they were not aware, and therefore, not careful to guard their tongues. The gleaned intel was then passed to couriers, of which Louise was one, to be transported by car, train, or on foot to the military leaders they worked for. It was a dangerous occupation, but the spies in the network wanted to serve in the war effort, and this was their chance.
Spies in “The Alice Network” and other such networks, went to work in jobs that were basically normal everyday jobs. They became waitresses, singers, shop workers, all in areas frequented by the enemy. They swallowed their disgust, in order to become almost invisible to the Germans. They never told anyone that they spoke German, because the Germans felt comfortable talking in front of these people who, they thought, couldn’t understand a word they said. It gave the spy networks just the edge they needed. Some spies, like Louise, spent time in makeshift hospitals writing letters in German dictated by dying Germans to their families. Dying men aren’t always careful with the information they give. A wealth of information was passed from these networks to the intelligence officers, and it often proved to be invaluable.
Louise lived with her sister, Germaine at 166 rue d’Isly. From October 4 to 13, 1914, by turning the only cannon that the Lille troops had, the defenders succeeded in deceiving the enemy and holding them for several days under an intense battle that destroyed more than 2,200 buildings and houses, particularly in the area of the station. Louise de Bettignies, aged 28, making full use of the four languages she spoke, including German and English. Through the ruins of Lille, she ensured the supply of ammunition and food to the soldiers who were still firing on the attackers. Then, since she had been a citizen of Lille since 1903, Louise made the decision in October 1914, to engage in resistance and espionage. Due in part to her ability to speak French, English, German, and Italian, she ran a vast intelligence network from her home in the North of France on behalf of the British army and the MI6 intelligence service under the pseudonym Alice Dubois. This network provided important information to the British through occupied Belgium and the Netherlands. The network is estimated to have saved the lives of more than a thousand British soldiers during the 9 months of full operation from January to September 1915.
“The Alice Network” of a hundred people, mostly in forty kilometers of the front to the west and east of Lille, was so effective that she was nicknamed by her English superiors “the queen of spies.” She smuggled men to England, provided valuable information to the Intelligence Service, and prepared for her superiors in London a grid map of the region around Lille. When the German army installed a new battery of artillery, even camouflaged, this position was bombed by the Royal Flying Corps within eight days. Another opportunity allowed her to report the date and time of passage of the imperial train carrying the Kaiser on a secret visit to the front at Lille. During the approach to Lille, two British aircraft bombed the train and emerged, but missed their target. The German command did not understand the unique situation of these forty kilometers of “cursed” front (held by the British) out of nearly seven hundred miles of front. One of her last messages announced the preparation of a massive German attack on Verdun in early 1916. The information was relayed to the French commander who refused to believe it. Incredible!!! After all her success, this worthless French commander refused to believe her. Idiot!!
Louise was arrested by the Germans on October 20, 1915 near Tournai. On March 16, 1916, in Brussels, she was sentenced to forced labor for life. After being held for three years, she died on September 27, 1918 as a result of pleural abscesses poorly operated upon at Saint Mary’s Hospital in Cologne. Her body was repatriated on February 21, 1920. On March 16, 1920 a funeral was held in Lille in which she was posthumously awarded the Cross of the Legion of Honor, the Croix de guerre 1914-1918 with palm, and the British Military Medal, and she was made an Officer of the Order of the British Empire. Her body is buried in the cemetery of Saint-Amand-les-Eaux.

 Every year, my husband, Bob and I go to the Black Hills to go hiking and just to enjoy the area. It’s close to our home in Casper, Wyoming, and it just never gets old. Our favorite tourist site there is Mount Rushmore, and we try to stop in there every year. Mount Rushmore is such a special place, filled with patriotism and honor, but there are things I didn’t know about this, my favorite monument.
Every year, my husband, Bob and I go to the Black Hills to go hiking and just to enjoy the area. It’s close to our home in Casper, Wyoming, and it just never gets old. Our favorite tourist site there is Mount Rushmore, and we try to stop in there every year. Mount Rushmore is such a special place, filled with patriotism and honor, but there are things I didn’t know about this, my favorite monument.
Gutzon Borglum was an amazing man. He designed and built Mount Rushmore between the years of 1927 and 1941. During the years of work, no one was ever killed, a credit to the safety measures put in place by Borglum. Originally the monument was planned as a tribute to the wild west, but Borglum had other ideas. Personally I like his ideas much better. A tribute to patriotism and honor is a much more fitting idea. The presidents Borglum chose were representative of specific aspects of history. His original plan was to carve the figures of these four men from head to waist, but with Borglum’s March 6, 1941 passing, came the beginning of the end of the monuments carving. Borglum’s son took over the carving, and at first it continued as normal, but the beginning of World War II greatly hampered things, and the monument was declared finished on October 31, 1941. Not only were the bodies of the presidents never finished, but Lincoln’s ear was also never finished. Somehow, Lincoln’s missing ear was something I never really noticed.
About 90% of the monument’s carving was done with dynamite. The dynamite stripped off the rough outer layers of stone, and then the minute details were finished by hand. In all, the workers blasted away more that 450,000 tons of rock. If you look below some of the viewing areas at the base of the mountain, you can still see the drill holes in the rock that was blasted away. It’s quite interesting to see how it was done. In all there were about 400 works who carved the mountain, being paid a modest wage of 45 to 75 cents an hour, for their 
 extraordinary efforts. These days he probably couldn’t have hired any workers for that wage, but those were very different times. These men worked very hard doing grueling work and didn’t complain. I believe they could see the vision of their boss, and I think most were proud to be a part of such an amazing project. In many ways, I wish the project could have been finished. I think the final design would have been an amazing work of art. Nevertheless, I love the mountain monument, finished or not.
extraordinary efforts. These days he probably couldn’t have hired any workers for that wage, but those were very different times. These men worked very hard doing grueling work and didn’t complain. I believe they could see the vision of their boss, and I think most were proud to be a part of such an amazing project. In many ways, I wish the project could have been finished. I think the final design would have been an amazing work of art. Nevertheless, I love the mountain monument, finished or not.
 For Corporal Charles Joseph Berry, March 3, 1945 was just another day in the trenches…at least that was how it began. By days end, the war would be all over for Corporal Berry…as would his life. At this point, many people would expect that Corporal Berry would be “just another war statistic,” and they would be right, to a small degree. Corporal Berry was a war statistic, but it was the way he died that changed everything…that made him a hero!!
For Corporal Charles Joseph Berry, March 3, 1945 was just another day in the trenches…at least that was how it began. By days end, the war would be all over for Corporal Berry…as would his life. At this point, many people would expect that Corporal Berry would be “just another war statistic,” and they would be right, to a small degree. Corporal Berry was a war statistic, but it was the way he died that changed everything…that made him a hero!!
Charles Joseph Berry was born on July 10, 1923 in Lorain, Ohio, and graduated from Clearview High School in Lorain in 1941. After graduation he went to work as a truck driver for a moving company. When World War II broke out, Corporal Berry enlisted in the Marine Corps in Cleveland, Ohio, on October 1, 1941. He was 18 years old. He was sent to Parris Island, South Carolina for basic training. Following his basic training, he was stationed to the Marine Barracks at Quantico, Virginia, but shortly afterwards was ordered to the Marine Barracks, New River, North Carolina, for parachute training. He was promoted to private first class on June 2, 1942, after qualifying as a parachutist.
On March 11, 1943, PFC Berry sailed from San Diego, California, arriving later that month in New Caledonia with the 1st Parachute Battalion. He left New Caledonia in September 1943, arriving in the Solomon Islands a few weeks after his departure. Then, in October 1943, he went to Vella La Vella, where he remained for one month. In November 1943, he landed at Bougainville, and during that campaign, took part in the raid at Koairi Beach and in the Empress Augusta Bay action. Prior to returning to the United States in February 1944, he spent a short time at Guadalcanal. Following his arrival at Camp Elliott, San Diego, he joined the newly organized 5th Marine Division in early 1944. In July he departed for the Hawaiian Islands with that division. He was advanced to corporal on July 22, 1944. He landed on Iwo Jima on D-Day, February 19, 1945.
On March 3, 1945, Corporal Berry was killed during a battle that would win him the Medal of Honor. Corporal Berry while stationed in the front lines, manned his weapon with alert readiness as he maintained a constant vigil with other members of his guncrew during the hazardous night hours of March 2nd. Infiltrating Japanese soldiers launched a surprise attack shortly after midnight in an attempt to overrun his position. Corporal Berry engaged in a pitched hand-grenade duel, returning the dangerous weapons with prompt and deadly accuracy until an enemy grenade landed in the foxhole. Corporal Berry gave no thought to his own safety, but determined to save his comrades, he unhesitatingly chose to sacrifice himself and immediately dived on the deadly grenade. His body absorbed the shattering violence of the exploding charge, and protected the others from serious injury. Corporal Berry had never given it another thought. He just did it, and then it was all over. He gave his life so that his fellow marines might carry on the relentless battle against a ruthless enemy, and “his superb valor and unfaltering devotion to duty in the face of certain death reflect the highest credit upon himself and upon the United States Naval Service.”
Corporal Berry was buried in the 5th Marine Division Cemetery on Iwo Jima, but was later reinterred in Elmwood Cemetery, Lorain, Ohio, in 1948. He was honored for “conspicuous gallantry and intrepidity at the risk of his life above and beyond the call of duty” as a member of a machine-gun crew, serving with the 1st Battalion, 26th Marines, 5th Marine.
 Milly Elise “Lise” Borsum was a Norwegian resistance member during World War II. Born on September 18, 1908 in Kristiania, she was the daughter of pianist and composer Eyvind Alnaes and his wife Emilie Thorne. She was married to physician Ragnar Borsum from 1930 to 1949, and was mother of actress Bente Borsum.
Milly Elise “Lise” Borsum was a Norwegian resistance member during World War II. Born on September 18, 1908 in Kristiania, she was the daughter of pianist and composer Eyvind Alnaes and his wife Emilie Thorne. She was married to physician Ragnar Borsum from 1930 to 1949, and was mother of actress Bente Borsum.
During the Holocaust, Lise and her husband had compassion on the Jewish people, making the fateful decision to harbor them from the Nazis. In April of 1943, Lise and her husband were arrested and incarcerated at the Grini concentration camp for two months. They had been members of a network which helped Jewish people escape to Sweden. On June 28, 1943, she was sent to Germany, with MS Monte Rosa from Oslo  to Arhus, and further with railway transport to Hamburg. She spent a short time at the Hütten Gefängnis in Hamburg before ending up as a Nacht und Nebel prisoner at the Ravensbrück concentration camp, which was a camp specifically for women. Nacht und Nebel was a directive issued by Adolf Hitler on December 7, 1941 targeting political activists and resistance “helpers” in World War II to be imprisoned or killed. Their families and the population usually knew nothing of their fate or whereabouts They were the Nazi state’s alleged offenders, often without trial or conviction or even charges. Victims who disappeared in these Night and Fog actions were often never heard from again. The prisoners usually had their heads shaved and their dignity removed in any horrific way
to Arhus, and further with railway transport to Hamburg. She spent a short time at the Hütten Gefängnis in Hamburg before ending up as a Nacht und Nebel prisoner at the Ravensbrück concentration camp, which was a camp specifically for women. Nacht und Nebel was a directive issued by Adolf Hitler on December 7, 1941 targeting political activists and resistance “helpers” in World War II to be imprisoned or killed. Their families and the population usually knew nothing of their fate or whereabouts They were the Nazi state’s alleged offenders, often without trial or conviction or even charges. Victims who disappeared in these Night and Fog actions were often never heard from again. The prisoners usually had their heads shaved and their dignity removed in any horrific way  imaginable to bring them into submission.
imaginable to bring them into submission.
She was held at Ravensbrück until April 8, 1945, when the surviving Scandinavian prisoners were transported home with the White Buses organized by the Swedish Red Cross. She was one of the blessed few who walked away alive from the concentration camps. Many prisoners, political or otherwise were killed, starved, beaten, or worked to death. Lise Borsum managed to live through it. Later in life, she was known for her writings and for organizing work after the war. She went on to live a long life, dying on August 29, 1985 at the age of 76. She had done her part to help the Jewish people during the Holocaust, and she was not sorry.

