 We all look for firsts in things, like first steps, first words, first man in space, first man on the moon, and in this case, the first around the world flight of a jet engine. You would expect that it might be some new jet, designed by an aviation expert, and you would be right, but the flight in question happened on January 16, 1957. The plans were three Boeing B-52 Stratofortresses. This was not just a flight for the purpose of setting a record, but rather it was a flight designed to prove a very important point. The operation was called Operation Power Flite…I’m not sure why flight was spelled flite. The planes made the trip around the world in 45 hours and 19 minutes, using in-flight refueling so that they could stay aloft for the entire journey. The mission was intended to demonstrate that the United States had the ability to drop a hydrogen bomb anywhere in the world. Led by Major General Archie J. Old, Jr. as flight commander, five B-52B aircraft of the 93rd Bombardment Wing of the 15th Air Force took off from Castle Air Force Base in California on January 16, 1957, at 1:00 PM, with two of the planes flying as spares. Old was aboard Lucky Lady III (serial number which was commanded by Lieutenant Colonel James H. Morris, who had flown as the co-pilot aboard the Lucky Lady II when it made the world’s first non-stop circumnavigation in 1949. Heading east, one of the planes was unable to refuel successfully from a Boeing KC-97 Stratofreighter and was forced to land at Goose Bay Air Base in Labrador. The second spare refueled with the rest of the planes over Casablanca, Morocco and then split off as planned to land at RAF Brize Norton in England.
We all look for firsts in things, like first steps, first words, first man in space, first man on the moon, and in this case, the first around the world flight of a jet engine. You would expect that it might be some new jet, designed by an aviation expert, and you would be right, but the flight in question happened on January 16, 1957. The plans were three Boeing B-52 Stratofortresses. This was not just a flight for the purpose of setting a record, but rather it was a flight designed to prove a very important point. The operation was called Operation Power Flite…I’m not sure why flight was spelled flite. The planes made the trip around the world in 45 hours and 19 minutes, using in-flight refueling so that they could stay aloft for the entire journey. The mission was intended to demonstrate that the United States had the ability to drop a hydrogen bomb anywhere in the world. Led by Major General Archie J. Old, Jr. as flight commander, five B-52B aircraft of the 93rd Bombardment Wing of the 15th Air Force took off from Castle Air Force Base in California on January 16, 1957, at 1:00 PM, with two of the planes flying as spares. Old was aboard Lucky Lady III (serial number which was commanded by Lieutenant Colonel James H. Morris, who had flown as the co-pilot aboard the Lucky Lady II when it made the world’s first non-stop circumnavigation in 1949. Heading east, one of the planes was unable to refuel successfully from a Boeing KC-97 Stratofreighter and was forced to land at Goose Bay Air Base in Labrador. The second spare refueled with the rest of the planes over Casablanca, Morocco and then split off as planned to land at RAF Brize Norton in England.
After a mid-air refueling rendezvous over Saudi Arabia, the planes followed the coast of India to Sri Lanka and then made a simulated bombing drop south of the Malay Peninsula before heading towards the next air refueling rendezvous over Manila and Guam. The three planes continued across the Pacific Ocean and landed at March Air Force Base near Riverside, California on January 18 after flying for a total of 45 hours and 19 minutes, with the lead plane landing at 10:19 AM and the other two planes following each other separated by 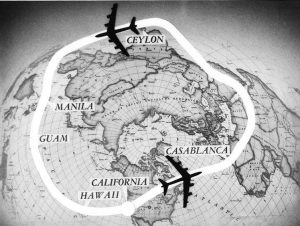 80 seconds. The 24,325 miles flight was completed at an average speed of 525 miles per hour and was completed in less than half the time required by Lucky Lady II when it made the first non-stop circumnavigation in 1949. General Curtis LeMay was among the 1,000 on hand to greet the three planes, and he awarded all 27 crew members the Distinguished Flying Cross. Though Old called the flight “a routine training mission,” the Air Force emphasized that the mission demonstrated its “capability to drop a hydrogen bomb anywhere in the world.” The flight was in reality, a warning to hostile nations, that the United States was capable of dropping a bomb anywhere in the world, and it would be for the best if these nations did not provoke the United States.
80 seconds. The 24,325 miles flight was completed at an average speed of 525 miles per hour and was completed in less than half the time required by Lucky Lady II when it made the first non-stop circumnavigation in 1949. General Curtis LeMay was among the 1,000 on hand to greet the three planes, and he awarded all 27 crew members the Distinguished Flying Cross. Though Old called the flight “a routine training mission,” the Air Force emphasized that the mission demonstrated its “capability to drop a hydrogen bomb anywhere in the world.” The flight was in reality, a warning to hostile nations, that the United States was capable of dropping a bomb anywhere in the world, and it would be for the best if these nations did not provoke the United States.


Leave a Reply